Modern Linux distributions come with the systemd initialization system that allows users to manage services with the systemctl command.
However, some older systems still use System V or Upstart. In that case, use the chkconfig command to list, start, and stop services, as well as enable or disable services from startup.
This guide will show you how to use the chkconfig command to control system services in Linux.

Prerequisites
- A system running System V or Upstart.
- Access to the terminal/command line.
- Access to an account with root or sudo privileges.
The chkconfig Command Syntax
The chkconfig command syntax looks like this:
chkconfig [options] [service] [subcommand]The command works on its own, but can also be used with:
- The
--list,--level,--add,--del, and--overrideoptions specified before the service name. The options print the details or manage the service. - The
on,off,reset, orresetprioritiessubcommands added after the service name. The subcommands change the startup info for the specified service.
The chkconfig Command Options
Running the chkconfig command without any options outputs the current configuration of all services:
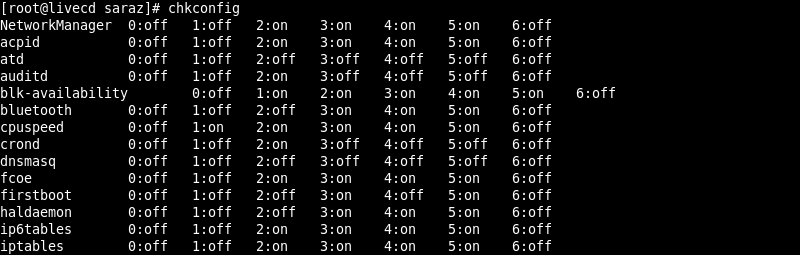
However, executing the command with different options and subcommands enables users to manage services rather than just list them. The table below shows the options and subcommands used with the chkconfig command:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
--list | Displays all services and their current startup status in each runlevel. |
--list | sort | Sorts services alphabetically and displays them with their current startup status in each runlevel. |
--list | grep on | Shows only running services and their current startup status in each runlevel. |
--list | grep off | Shows only services disabled in one or more runlevels and their current startup status in each runlevel. |
--list | grep --level <levels>:on | Level-specific: Prints services running in a particular runlevel. |
--list | grep --level <levels>:off | Level-specific: Prints services that are disabled in a certain runlevel. |
--list [service] | Outputs the status of a particular service in each runlevel. |
[service] on | Enables a service to start on system boot. |
[service] off | Disables a service from starting on system boot. |
--level <levels> [service] on | Turns on a particular service across one or more runlevels. |
--level <levels> [service] off | Turns off a particular service in single or multiple runlevels. |
--add [service] | Adds a service to startup in all runlevels. |
--del [service] | Removes a service from the startup in all runlevels. |
[service] reset | Resets the on/off statuses of all services. |
[service] resetpriorities | Resets the start/stop priorities of all services. |
--override [service] | Reconfigures a service to the override settings instead of the default configuration. |
The chkconfig Command Examples
The chkconfig command is the ultimate service management tool for older Linux systems. The sections below outline common chkconfig examples.
List All Services
To list all services, execute the command without options or run:
chkconfig --list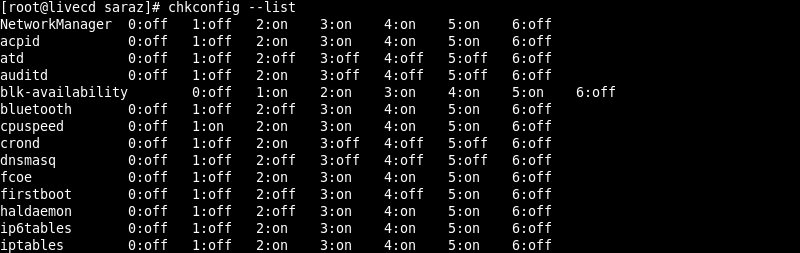
Using --list with the chkconfig command displays the status of all available services in all runlevels. In case you want to sort services in alphabetical order, use the sort option:
chkconfig --list |sort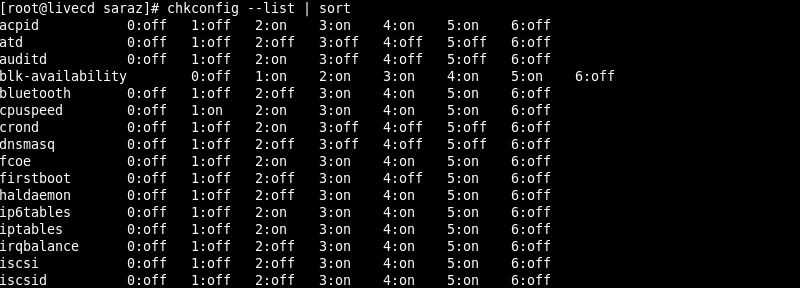
The chkconfig --list command also works in RHEL 7. However, the output only displays Sys V services and not native system services:
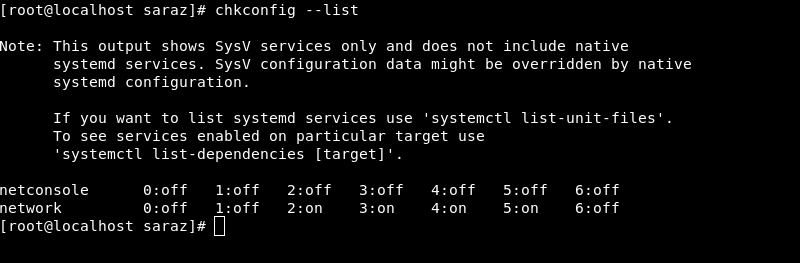
List All Enabled Services
To find all enabled services (in one or multiple runlevels), execute combine chkconfig --list with the grep command:
chkconfig --list | grep on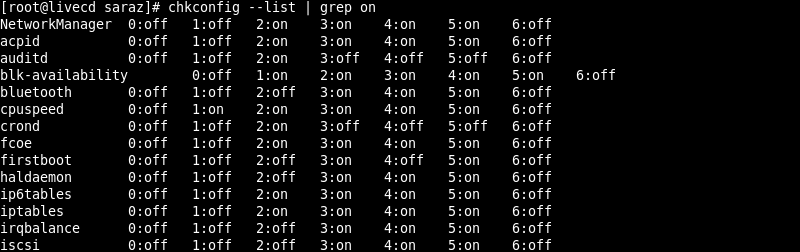
To find all disabled services (in one or multiple runlevels), run:
chkconfig --list | grep off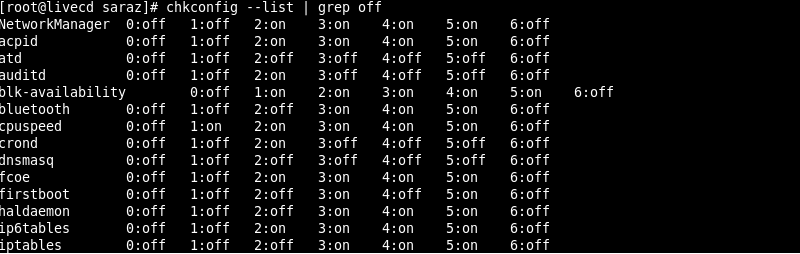
Furthermore, to narrow down the scope to the services on/off a particular runlevel, use:
chkconfig --list | grep --level <levels>:onchkconfig --list | grep --level <levels>:offFor example, list all the services running in runlevel 5 with:
chkconfig --list | grep 5:on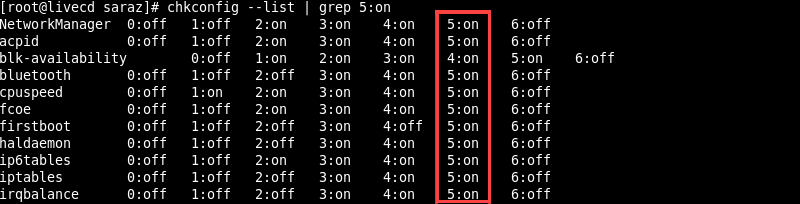
On the other hand, to display all the services that are not running in runlevel 5, execute:
chkconfig --list | grep 5 :off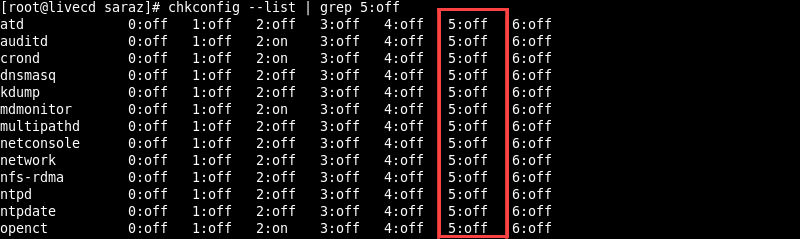
List a Particular Service
To show the startup configuration of a particular service in all runlevels, run chkconfig --list and specify the service.
chkconfig --list [service]For example, check the status of the ntpd service in all runlevels with:
chkconfig --list ntpd
The output shows that the ntpd service is disabled on boot in any runlevel.
Enable a Service
Enable a service to start on boot with the chkconfig [service] on command. Next, confirm that the service is on using <strong>--list</strong>.
chkconfig [service] on
chkconfig --list [service]
The on option affects runlevels 2, 3, 4, and 5 and starts the ntpd service on boot on these runlevels. To enable a service on one or multiple runlevels only, run:
chkconfig --level <levels> [service] onFor example, start the ntpd service on the third runlevel and verify the service’s configuration with:
chkconfig --level 3 ntpd on
chkconfig --list ntpd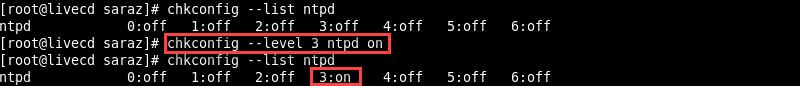
Similarly, to turn on the ntpd service in multiple runlevels in one go use:
chkconfig --level 235 ntpd on
chkconfig --list ntpd
Disable a Service
Disable a service from starting at system boot with the chkconfig [service] off command:
chkconfig [service] off
chkconfig --list [service]
Even though the off variable also affects runlevels 2 to 5, users can specify in which runlevels to disable a service.
For instance, disable the ntpd service only in runlevel 3 and verify the results with:
chkconfig --level 3 ntpd off
chkconfig --list ntpd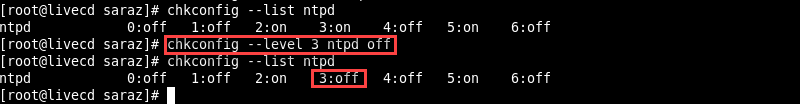
Add a Service
Add a service to startup in all runlevels with the following command:
chkconfig --add [service]For example, use the --add option to add ntpd to startup in all runlevels. Next, use --list to verify the service has been added:
chkconfig --add ntpd
chkconfig --list ntpd
The chkconfig command adds and configures the service as specified by the default values in the init script. For example, the ntpd service is disabled by default in every runlevel.
Note: The command adds a service only if its available and installed. If the service has not been installed, install its package first.
Remove a Service
Remove a service from startup in all runlevels with the --del option:
chkconfig --del [service]
The --del option removes the service from startup, but the service remains in the system. Therefore, to add the service back to startup, use the --add option again.
Reset Service Configuration
To reset the on/off status of a service in all runlevels as specified in the init script, execute:
chkconfig [service] reset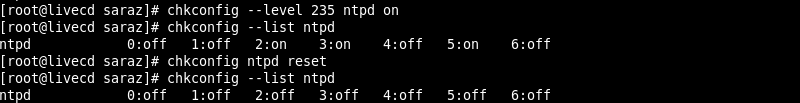
The output shows that ntpd returns to the default off status in all runlevels.
Conclusion
After reading this tutorial, you know how to use the chkconfig command to manage services in older versions of Linux.
Next, learn how to use the systemctl command to start, stop, and restart Linux services on newer Linux distributions.