CGI-bin is a standard mechanism for executing server-side scripts in response to web requests. It remains especially relevant in environments where low-level control or legacy support is required.
In this tutorial, you will learn what CGI-bin is and how it works.

What Is CGI-bin?
CGI-bin is a directory on a web server designated for storing and executing CGI scripts. Common Gateway Interface (CGI) is a standard that enables the server to communicate with external programs, allowing them to process input and return output through the web. These scripts are used to generate dynamic content, such as form submissions, search results, or image processing.
The "bin" in CGI-bin stands for binary and references the executable nature of the scripts that the directory stores. When a request is sent to a CGI script, the web server passes it to the appropriate program in the CGI-bin directory, which processes the input and returns a response to the browser.
How Does CGI-bin Work?
When a user interacts with a web page that relies on server-side processing, e.g., submits a contact form or performs a search, the browser sends an HTTP request to the web server. The server examines the request and, if it determines that a CGI script should handle it, it looks for the script in the designated CGI-bin directory.
Once the correct script is located, the server executes it. The script processes the input data, performs any necessary operations (queries a database or generates dynamic content), and returns output in a format the web server can send back to the browser. The server then forwards the output to the user's browser, where it is displayed as part of the web page.
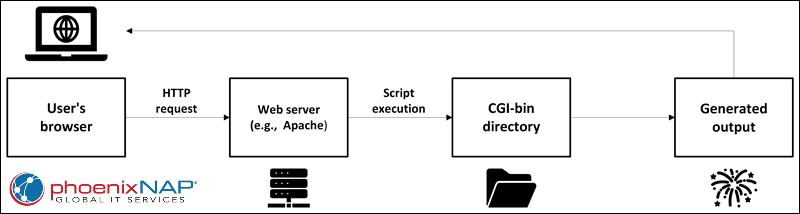
CGI scripts can be written in different languages, including Perl, Python, or compiled binaries, as long as they conform to the server's CGI execution environment. This mechanism allows websites to provide interactive features and dynamic content by executing code in response to user actions.
Why Is CGI-bin Important?
CGI-bin plays a key role in enabling server-side processing and dynamic content generation on websites. It provides a structured and secure location for scripts that handle user input, automate tasks, and deliver personalized responses.
While newer technologies have emerged, CGI-bin remains important for various reasons, especially in legacy systems and specialized server-side apps.
Some key points are:
- Dynamic content generation. CGI scripts generate HTML dynamically based on user actions or server data, allowing websites to display real-time updates, personalized messages, or interactive elements.
- Data processing. Scripts in the CGI-bin directory handle form submissions, process input on the server, and return relevant results. This is critical for features like contact forms, registrations, and search functions.
- Server-side execution. CGI scripts run on the server rather than in the browser, which reduces client-side load and enhances performance and security.
- Automation and customization. Developers can use CGI-bin to automate routine tasks or implement custom features, such as content updates, user tracking, or admin functions.
- Language flexibility. CGI-bin supports various programming languages (e.g., Perl, Python, C), making it accessible to a wide range of developers and use cases.
- Legacy and compatibility. Many existing systems and older websites still rely on CGI-bin for essential operations. Understanding it helps maintain and troubleshoot these systems.
CGI-bin may not be as prominent in modern web stacks, but its ability to handle input, produce dynamic output, and integrate seamlessly with web servers continues to make it a relevant and practical solution in many scenarios.
What Is CGI-bin Directory?
The CGI-bin directory is a specific folder on a web server that contains executable scripts. The scripts are executed when dynamic content generation needs to be handled. It acts as a bridge between the web server and external programs or databases, allowing websites to perform tasks beyond displaying static web pages.
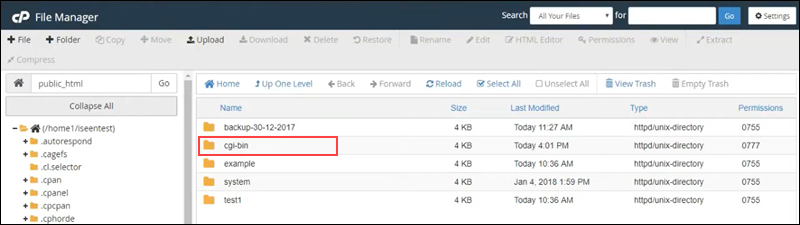
Follow the steps below to find and access the directory:
1. Log in to your hosting account.
2. Open the File Manager (usually found in cPanel).
3. Navigate to the public_html or www directory.
4. Look for a folder named cgi-bin. It may be at the root level of your web directory or inside public_html. Upload or manage your CGI scripts from there.
Alternatively, you can SSH into the server and access the directory via the terminal:
1. Use the syntax below to SSH into the server:
ssh username@your-server-ip2. Navigate to the web root with the cd command. This is commonly in one of the two locations:
/var/www/cgi-bin/or
/usr/lib/cgi-bin/3. Use commands like ls and nano to view the directory contents.
How to Use CGI-bin Directory
To use the CGI-bin directory, place the executable script files inside it, ensure proper permissions, and access them via a browser or internal server call. Scripts placed in CGI-bin must follow specific conventions. For example, they need the correct shebang line (e.g., #!/usr/bin/perl) and have appropriate permissions (typically 755).
File extensions like .cgi or .pl are commonly used, but this depends on the server configuration. Once placed in the cgi-bin directory, run the scripts via a URL.
How to Enable CGI-bin?
Enabling CGI on a web server means configuring it to recognize and execute scripts located in the cgi-bin directory. CGI support is disabled by default in many Apache installations, and in some modern stacks, other options like FastCGI or mod_python are used.
To allow CGI functionality, the server must be explicitly configured to treat files in the cgi-bin directory as executable programs. This involves enabling CGI-related modules and adjusting directory permissions and handlers.
Follow the steps below to enable CGI-bin on Debian/Ubuntu Apache servers:
1. Enable the CGI module with:
sudo a2enmod cgi
sudo systemctl restart apache22. Open the Apache configuration file with a text editor:
sudo nano /etc/apache2/apache2.conf3. Find the following section in the file:
ScriptAlias /cgi-bin/ /usr/lib/cgi-bin/
<Directory "/usr/lib/cgi-bin">
AllowOverride None
Options None
Require all granted
</Directory>Modify the Options section to be the same as below to allow execution in the CGI directory:
Options +ExecCGI
AddHandler cgi-script .cgi .pl .py4. Restart Apache to apply the changes:
sudo systemctl restart apache2Note: If you are using a RHEL-based system, the main Apache config file is usually /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf, and the systemctl service name is httpd instead of apache2.
How to Create cgi-bin Directory
If your server does not already have a cgi-bin directory, you can create one manually. Follow the steps below:
1. SSH into your server or use a file manager.
2. Create the directory with mkdir if you are using the terminal:
mkdir /usr/lib/cgi-bin3. Set the proper permissions with chmod:
chmod 755 / /usr/lib/cgi-bin4. Configure your web server to recognize and allow script execution in this directory by following the steps from the previous section.
How to Test cgi-bin Directory
To test if your cgi-bin directory is working, create a test script named test.cgi and execute it. Follow the steps below:
1. Open a text editor and paste the following content:
#!/usr/bin/perl
print "Content-type: text/html\n\n";
print "<html><body><h1>CGI is working!</h1></body></html>";2. Save the file as test.cgi and upload it to your cgi-bin directory.
3. Set executable permissions:
chmod +x test.cgi4. Open a web browser and navigate to the following web page:
https://yourdomain.com/cgi-bin/test.cgiReplace yourdomain.com with your actual web page domain.
If configured properly, you should see a web page displaying: "CGI is working!"
Conclusion
This tutorial explained how CGI-bin works, why it is important, and how to enable it on your server. Use the CGI-bin directory for a structured and reliable way to run server-side scripts, enabling dynamic content and user interaction on websites.
Next, read our Linux server guide or see how to install Apache web server on CentOS and Rocky Linux.