Unused software packages slow down system performance, not only by consuming valuable storage space but also by negatively affecting overall performance. For an efficient CentOS environment, it is best practice to easily identify and remove any specific software that is no longer required.
In this tutorial, learn how to remove packages and uninstall dependencies from CentOS.
Prerequisites
- Access to a user account with sudo or root privileges.
- Command-line access.
Uninstall Package from CentOS with Yum
CentOS is an RHEL (Red Hat Enterprise Linux) distribution. Users rely on the RPM and YUM package managers for installing and removing software packages.
To remove a package from CentOS, use the following YUM command:
yum remove [package_name]Alternatively, use the erase subcommand:
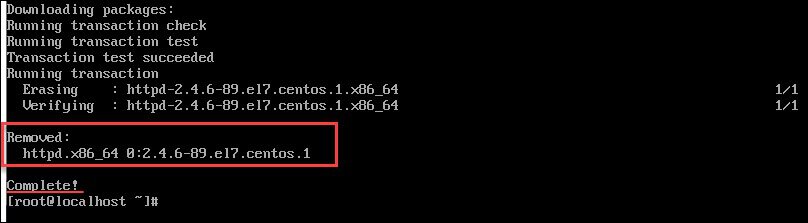
yum erase [package_name]The following example removes the Apache web server package named httpd.x86_64, using YUM:
yum remove httpd.x86_64Before removing, the command prompt asks for the root (or sudo user) password, and confirmation that you want the software deleted.
Type in y (for yes) and press Enter.
Finally, the output shows that the process is complete and lists the deleted package(s).
Note: Only root users and users added to the sudousers group have permission to install and remove packages in CentOS.
How to Remove Packages with Dependencies Using Yum
Package dependencies are binaries, libraries, and modules on which software relies. When installing software, it automatically downloads and installs the required dependencies.
In most cases, deleting software from the local package manager will also erase its dependencies (unless other programs require them).
Still, there are instances where these dependencies must be removed manually.
To remove a package and erase all the unneeded dependencies, use the following command:
yum autoremove [package_name]Note: When a user installs a package, YUM downloads and stores it in /var/cache/yum. However, packages remain in cache even after they've been installed and removed. In time, the stored cache may take up too much disk space or cause issues due to corrupt metadata. To reclaim disk space, be sure to clean the YUM cache.
Alternatively, you can alter the yum configuration file to automatically remove package dependencies when deleting a package with the yum remove or yum erase commands:
1. Open the yum.conf file with a text editor of your choice:
vi /etc/yum.conf2. Add the following line to the file:
directive clean_requirements_on_remove=1
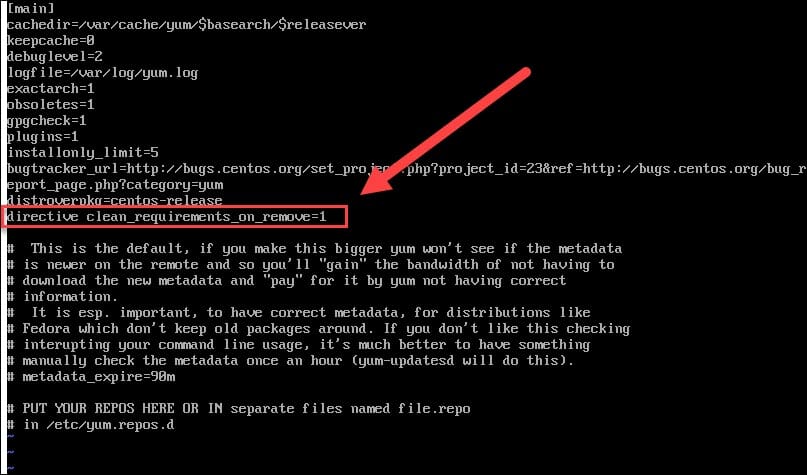
Save and exit the file.
How to Find Specific File in CentOS
In case you need to delete a package but are unsure of its exact file name, use the following command:
yum list- | grep [package_name]Alternatively, enter the command below:
rpm -qa | grep [package_name]The output will list all installed packages whose file names contain the specified phrase.
As you can see in the image below, httpd appears in the following packages (and dependencies):
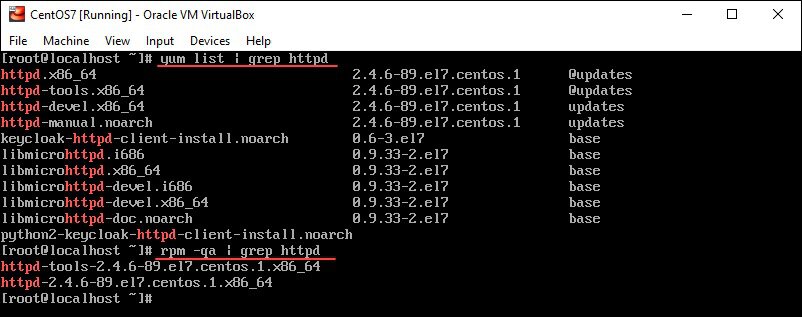
Once you have the exact name of the package you want to uninstall, you can remove it from your CentOS system.
For more options on listing packages on CentOS read our detailed tutorial.
Conclusion
After reading this tutorial, you should now know how to remove packages and dependencies to free up space taken up by redundant programs.
You also know how quickly find specific packages or files you want to delete.