The Domain Name System (DNS) stores domain information and maps domain names to IP addresses, allowing web browsers and other applications to locate and connect to relevant resources.
When a domain owner modifies a DNS record (e.g., during a host migration or email settings updates), the changes must propagate across the Internet to become available for all users.
This article outlines DNS propagation mechanisms and verification methods and offers guidance on how to speed up the process.

What Is DNS Propagation?
DNS propagation is the process of updating domain DNS records across the global DNS server network. When a domain's information changes (e.g., server location, A records, or MX records), authoritative DNS servers must pass the new instructions to recursive DNS resolvers, internet service providers (ISPs), and network operators globally.
Until complete propagation, users may encounter issues stemming from outdated DNS information, including:
- Connecting to stale content. If the DNS records point to a server that is no longer the primary host, users may receive an old version of a website.
- Connection timeouts. If the browser repeatedly attempts to connect to an incorrect or unresponsive IP address, the connection eventually times out.
- Email delays. Emails may experience significant delays if they are trying to reach an unresponsive or incorrect email server due to outdated MX records. In severe cases, the result may be an undeliverable message that bounces back to the sender.
- Software connectivity issues. Applications and services rely on DNS to locate their backend servers or other network resources. Outdated DNS can prevent these applications from functioning correctly.
- Authentication issues. Some authentication protocols rely on DNS lookups for verification. Outdated records can lead to authentication failures.
How Does DNS Propagation Work?
The DNS system operates hierarchically. When a user enters a domain name in a browser, the following steps occur:
- The client checks the local DNS cache. If the system finds an entry, it uses the cached record.
- If the entry is not found locally, the client queries a recursive DNS resolver, typically provided by an ISP.
- Recursive resolver queries a root DNS server.
- The root server directs the resolver to the appropriate Top-Level Domain (TLD) server (e.g., .com, .org).
- The TLD server directs the resolver to the domain's authoritative name servers, which hold current DNS records.
- The authoritative name servers provide the domain's associated IP address.
- Recursive resolver caches this information for a specified Time-to-Live (TTL), and the client also caches it.
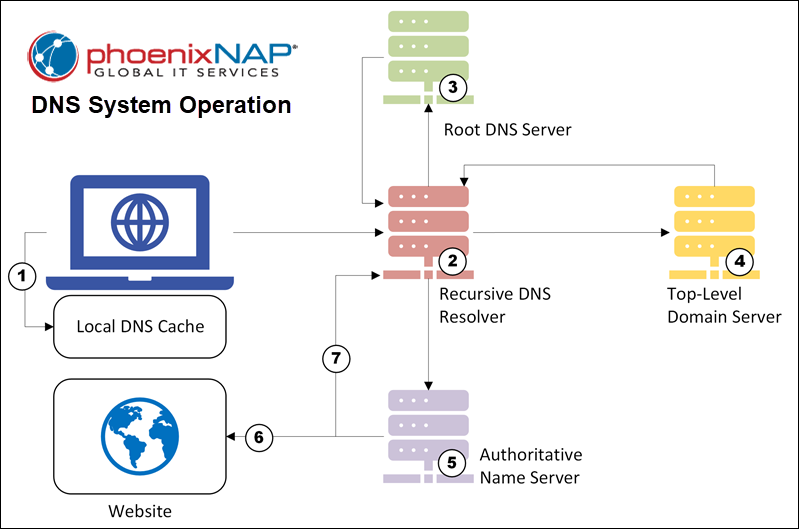
When DNS records change, new information replaces old information in these various internet caches. This cache update process constitutes DNS propagation.
What Influences DNS Propagation Time?
The speed at which DNS record updates become globally visible is not fixed but is instead influenced by several variables.
Below is the list of factors influencing DNS propagation time:
- Time-to-Live (TTL). Each DNS record has a TTL, representing cache duration for DNS resolvers before re-querying. A higher TTL results in longer caching and slower propagation of changes. Lower TTL results in more frequent checks and accelerates the propagation process.
- ISP caching policies. ISPs and network providers implement different caching policies and update frequencies.
- Geographic location. The physical distance between DNS servers can affect the speed, with users closer to updated servers observing changes more quickly.
- DNS record type. Changes to specific record types (e.g., NS records) may have a broader propagation impact than simple A record changes.
- DNS resolver behavior. Some DNS resolvers may not strictly adhere to TTL values, refreshing caches at more or less frequent intervals than specified.
Note: Incorrect or delayed DNS record propagation can trigger errors on the DNS server. Read our article to learn how to fix the "DNS Server Not Responding" error.
How to Check DNS Propagation?
Ensuring DNS record updates have successfully propagated across the internet is a critical post-modification step. Due to the decentralized and cached nature of DNS, propagation requires the following methods to verify:
- Online propagation checkers. Web-based tools that query diverse global DNS servers can provide a geographical overview, indicating which regions reflect the new records versus stale data.
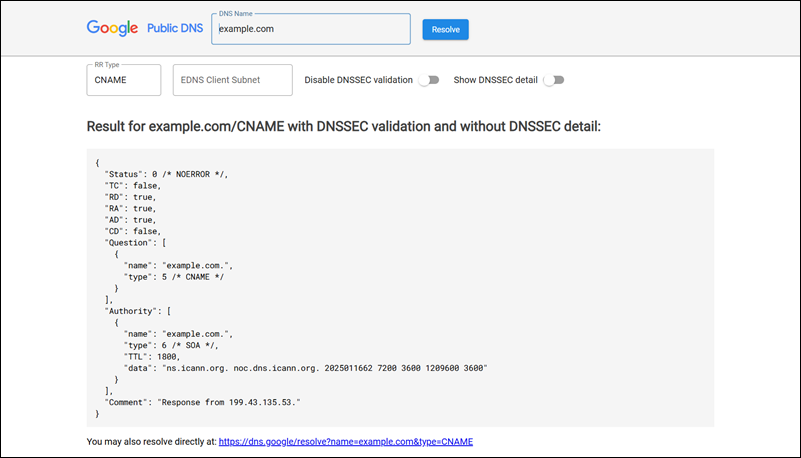
- Command-line utilities. The nslookup command can query a specified DNS server for record resolution, while the dig command provides verbose DNS query response data.
- Local DNS cache flushing. Cleaning the operating system's DNS resolver cache eliminates the influence of locally cached content.
Popular DNS Propagation Checkers
The most popular tools for checking DNS propagation include:
- WhatsMyDNS.net. A user-friendly, global DNS server query tool for various record types.
- DNSChecker.org. A global server checker with a clear and intuitive interface.
- DNSMap.io. A tool for visual representation of DNS propagation on a world map.
- IntoDNS.com. A DNS records analyzer that highlights potential issues, including caching and authoritative server configurations.
- dns.google. A simple DNS checker made by Google.
How to Speed Up DNS Propagation?
Instant global DNS record updates are impossible to perform due to physical limitations.
However, use the strategies below to accelerate the process or minimize downtime during DNS changes:
- Lower TTL before the change. Reduce the TTL values of relevant records before anticipated DNS modifications such as website migrations. For instance, decrease the A record TTL from 24 hours to 5 minutes (300 seconds) one to two days in advance. The shorter cache time accelerates the propagation of new records. Revert to a higher TTL post-propagation to reduce DNS queries.
- Coordinate changes during off-peak hours. Schedule DNS changes during periods of lowest website traffic to minimize impact on users.
- Use a reliable DNS provider. A well-distributed DNS provider network contributes to faster and more consistent propagation.
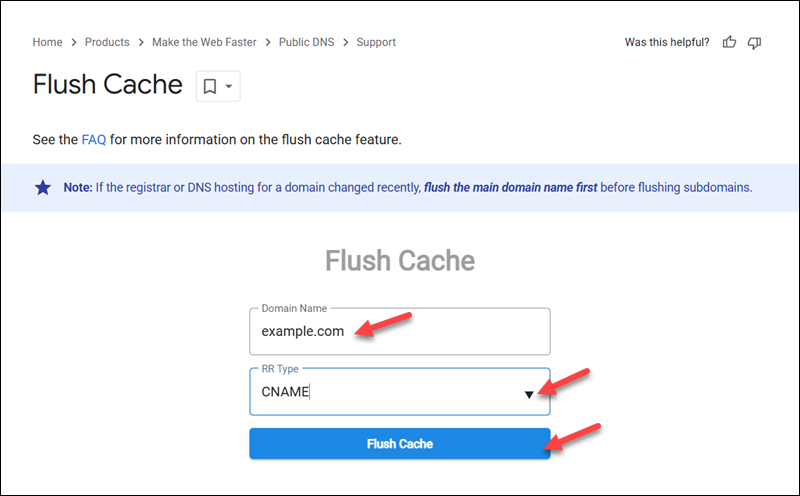
- Flush the public DNS cache. Accelerate DNS propagation by flushing the DNS cache from widely used public databases, such as Google or OpenDNS. For example, to perform this action on Google, go to the Flush Cache page on the Google Public DNS website, enter a domain name and a record to flush, and press Flush Cache.
- Clear local DNS cache. Flush the DNS cache for immediate change visibility on the local machine.
- Force-refresh browser DNS cache. Clear the browser cache or restart the browser to refresh its DNS cache.
DNS Propagation Best Practices
Proper DNS management minimizes downtime during record changes and ensures quick, consistent updates across the network. Following best practices involves careful planning and proper handling of DNS record settings.
To ensure optimal DNS propagation, implement the following best practices:
- Plan ahead. Always pre-plan DNS changes, especially for critical services.
- Test thoroughly. Test new configurations in a staging environment before significant changes.
- Communicate changes. Inform users or stakeholders about potential temporary disruptions that may occur.
- Monitor propagation. Actively monitor propagation progress after changes.
- Maintain consistent TTLs (post-propagation). After propagation completion, set TTLs to reasonable values (e.g., 1-4 hours) to balance performance and future change flexibility. Very low TTLs can increase DNS query load.
Conclusion
After reading this article, you understand how DNS updates propagate and the problems outdated records create. Applying these methods for checking propagation and following best practices will help you maintain stable and efficient network services.
To keep your infrastructure secure and reliable, learn about the 15 DNS Best Practices.



