Nginx (pronounced Engine X) is a popular, open-source HTTP web server, used for hosting high-traffic websites. It’s faster and requires fewer resources than other web servers.
The software uses a scalable event-driven (asynchronous) architecture, approaching requests one at a time. Apart from a web server, it also works as a reverse proxy, mail proxy, HTTP cache, and a load balancer.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to install Nginx on CentOS 8.

Prerequisites
- A CentOS 8 operating system
- A server IP or domain to connect to your Nginx web server
- A user with root privileges
- SELinux set up properly
Install Nginx on CentOS 8
Before any installation, always update the local repository to ensure you are downloading the latest software. Use the command:
sudo yum updateYou can inspect the Nginx package before adding it to your system. Request to see the RPM metadata included in every RPM package:
sudo yum info nginx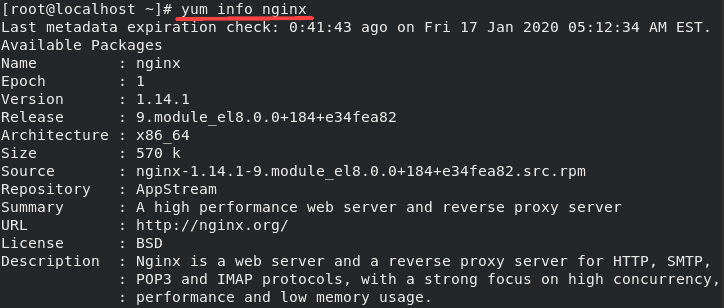
Next, install Nginx on CentOS 8 with the command:
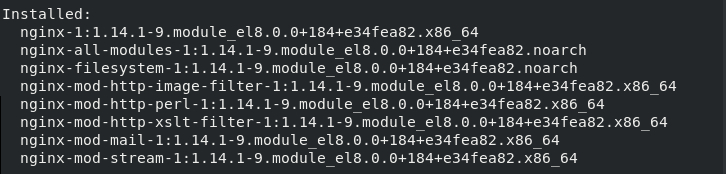
sudo yum install nginxThe output shows you a list of Nginx packages that have been installed, as in the image below.
Note: Nginx is a well-known web server alternative to Apache. If you are still unsure which one would be best for your website, you may want to check out this quick comparison between Apache and Nginx.
Start Nginx on Centos 8
Although you have installed Nginx, the service will not start automatically.
Start the service by typing:
sudo systemctl start nginxTo enable the service to start running upon boot time use:
sudo systemctl enable nginxIf you check the service status, the output should show you Nginx is active (running):
sudo systemctl status nginx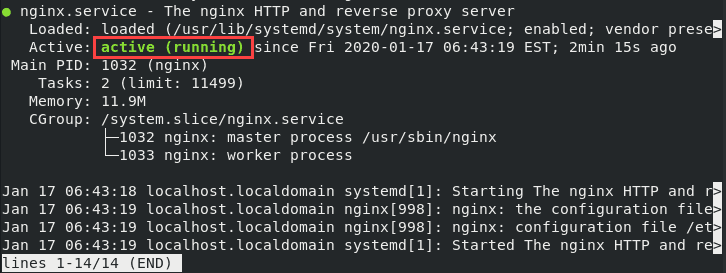
Stop, Reload or Restart Nginx
Stop Nginx using the command:
sudo systemctl stop nginxRestart Nginx (stop and start the service again) with the command:
sudo systemctl restart nginxReload the configuration files without stopping the service:
sudo systemctl reload nginxAdjust Firewall
Nginx includes firewalld service files that specify the service uses ports 80 (HTTP) and 443 (HTTPS) for web traffic. Therefore, you need to open and enable these ports to allow permanent access.
Open port HTTP and HTTPS with the commands:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http --add-service=httpssudo firewall-cmd --reloadsudo firewall-cmd --list-services --zone=publicTest the Firewall
Use Netstat to list all open ports and verify whether you have successfully opened 80 and 443:
netstat -tulpnDouble-check Nginx is working by visiting your public IP address (or domain name).
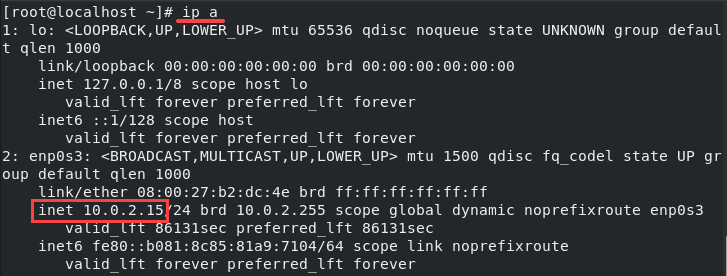
To see the IP address of your server, type the following command in the terminal:
ip addrFind the IP address and copy it.
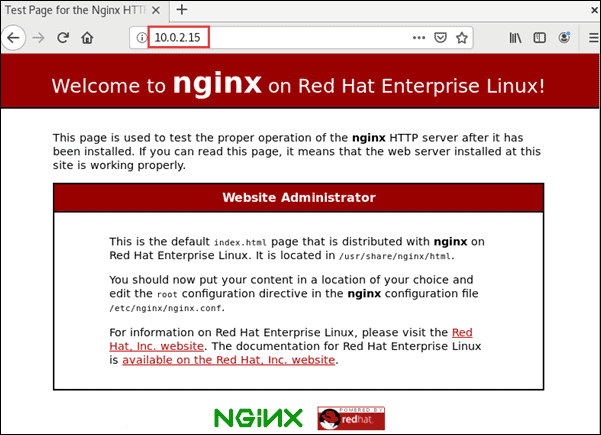
Then, open a web browser and paste the IP address (or domain name) in the URL bar. This should open the Nginx Welcome Page, confirming you have successfully installed and set up the server.
Configure Nginx
You don’t need to configure Nginx upon installation. However, you should know the location of the configuration files and the Nginx root directory in case you need to modify the configuration.
- Nginx configuration directory: /etc/nginx
- Nginx root directory: /usr/share/nginx/html
- Master/Global configuration file: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
If you wanted to change the Global configuration file, you would open it (etc/nginx/nginx.conf) with a text editor and apply the changes.
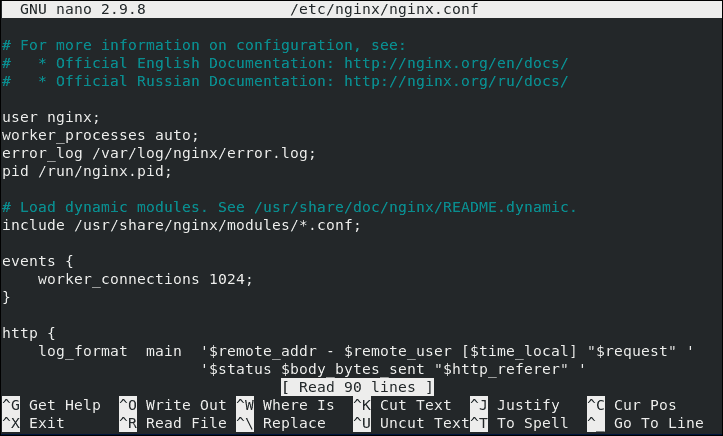
One common use case is editing the Nginx configuration file to redirect HTTP traffic to HTTPS.
Conclusion
You should now know how to install Nginx on CentOS 8.
Nginx is part of the LEMP stack, a collection of open-source software used for developing web applications and websites. LEMP is a popular alternative to the traditional LAMP stack. The only difference between the two is that the first uses Nginx, while the second one uses Apache as its web server.