Introduction
Being able to access information about a Helm release is important for maintaining a Kubernetes cluster. Helm does not feature a command that displays release logs. However, similar results can be achieved using two other commands.
This tutorial will teach you how to use helm history and helm list to obtain information about your Helm releases.
Prerequisites
- Kubernetes cluster (or minikube)
- Helm installed
Using helm history to Display Changes Made to a Release
The helm history command displays historical revisions of a release. To see the history for any release, type:
helm history [release-name]The output of this command is a table, as in the image below.
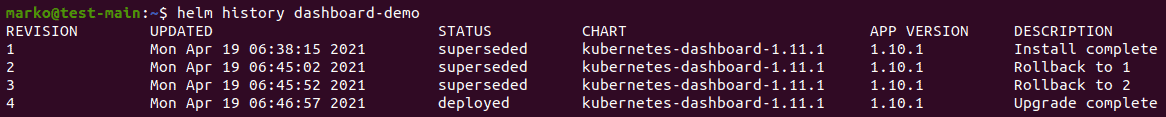
The table features revision numbers, the date and time of the revision, its status, the name of the release chart, the version of the app, and a description. The description column contains information about installation, upgrades, and rollbacks.
The default maximum of releases shown is 256. To limit the number of releases to a smaller number, use the --max argument:
helm history [release-name] --max [integer]
With the --max argument, Helm displays only the specified number of latest revisions.
Note: To print the output in a format other than the table, use the -o option followed by the format type. Other allowed formats are yaml and json.
Using helm list to Filter Release Information
The helm list command lists all the releases in the current namespace unless a different namespace is specified with the -n option. To search for a particular release, use the --filter option followed by a Pearl compatible regular expression:
helm list --filter '[expression]'The output of the command is by default a table, but yaml and json formats are also available via the -o option:
The command displays only deployed and failed releases. Use flags to see other types. For example, to see superseded releases, type:
helm list --filter '[expression]' --superseded
Other flags that you can use to filter releases include:
--all– Shows all releases without applying any filters.--deployed– This is the default option, applied if no other options are specified. It displays the releases that are currently deployed.--failed– Shows failed releases.--pending– Shows the releases pending deployment.--uninstalled– Displays releases uninstalled with the--keep-historyflag enabled during the uninstallation process.--uninstalling– Shows releases that are currently being uninstalled.
The flags can also be combined for a more detailed search.
Finally, the helm list output is sorted alphabetically. To sort the entries by date, use the -d (--date) argument:

Note: Sometimes, upgrading your release can produce the “helm has no deployed releases” error. Learn how to fix it.
Conclusion
While Helm does not have a dedicated logs command, you can combine helm history and helm list features to obtain the necessary information about a release.
For more useful Helm commands, check Helm Command Cheat Sheet.