The clear command is the go-to tool for clearing the terminal screen in Linux. Despite its effectiveness, clear does not reinitialize the terminal, which is sometimes necessary. Some alternative methods provide this option.
Read this tutorial to learn how to clear the terminal in Linux using different methods.
Prerequisites
- A Linux system (this tutorial uses Ubuntu 22.04).
- Access to the terminal.
How Do I Clear the Screen in Linux?
There are several methods to clear the screen in Linux. The following text elaborates on them.
Method 1: Clear the Screen in Linux via clear Command
The fastest way to clear the terminal screen in Linux is with the clear command. In most terminal emulators, like GNU, running clear without any arguments creates a blank slate screen:
clear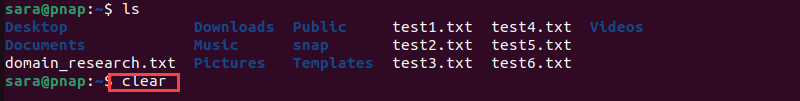
Once executed, the command clears up the terminal:

The command deletes everything, including the scrollback buffer. To keep the scrollback buffer, use clear with the -x argument:
clear -x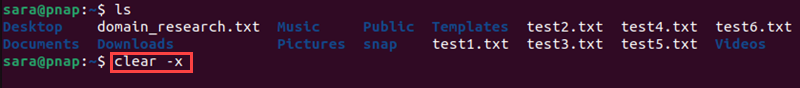
The clear -x command clears the terminal and keeps the previous output. Scroll up or use the PgUp button to view it:
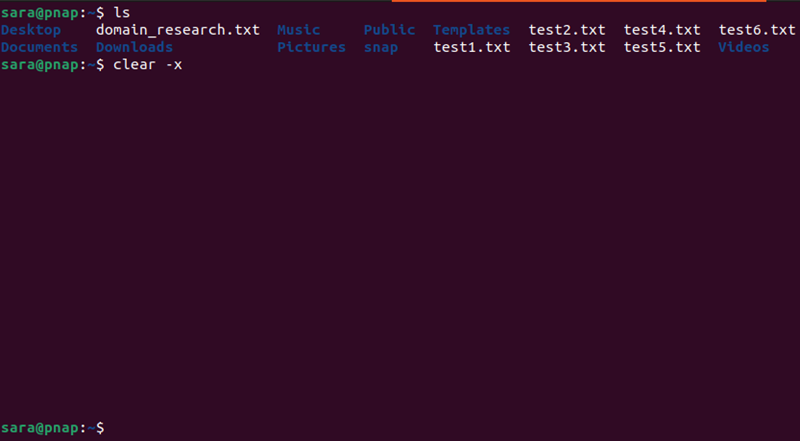
Additionally, the clear command does not reset the terminal. The shell state remains the same as before.
Method 2: Clear the Screen in Linux via reset Command
Unlike clear, the reset command reinitializes the terminal and restores default settings. To clear the terminal with this command, run:
reset
Executing reset takes a few moments to complete while clear shows effect instantly.
Method 3: Clear the Screen with Keyboard Shortcuts
Keyboard shortcuts also clear the terminal, depending on the terminal emulator.
In GNOME, the Ctrl + l shortcut has the same effect as clear -x. The shortcut clears the terminal while leaving the scrollback buffer:

To access command output history, use PgUp or scroll up:
In some terminal emulators, an alternative is Ctrl + Shift + K. The command provides the same output as Ctrl + L.
Method 4: Clear Terminal via alias Command
Alternative methods for clearing the terminal are also more complicated. For instance, the \033 is the ASCII escape character used to start terminal control sequences. When followed by c, the command clears the terminal.
printf "\033c"
The command clears the terminal screen, including the scrollback buffer.

To avoid typing numbers, create an alias for the command. For instance, set x as an alias for printf "\033c" with:
alias x='printf "\033c"'
Once the alias is created, running x results in a clear terminal screen.
Conclusion
This article explained how to clear the terminal screen using a few different methods.
Next, check out the ultimate guide of all Linux commands everyone should know.


