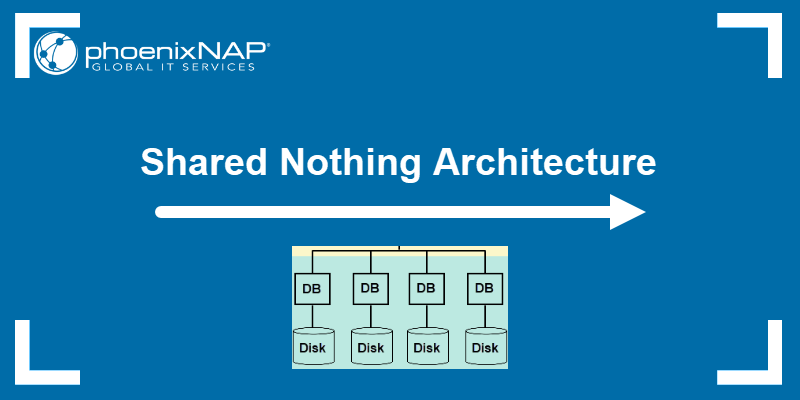
COLOCATION
BARE METAL CLOUD
HYBRID CLOUD
Hybrid Cloud
OverviewObject Storage
S3 Compatible Storage SolutionBare Metal Cloud
API-Driven Dedicated ServersAlternative Cloud Provider
Overcome Public Cloud LimitationsBackup Solutions
Veeam-Powered ServicesDisaster Recovery
VMware, Veeam, ZertoVeeam Cloud Connect
Backup and ReplicationManaged Backup for Microsoft 365
Veeam-Powered Service
NETWORK
LEARN