The whoami command is a part of the GNU coreutils project. The command allows Linux users to see who is currently logged in. The output displays the effective username in the current shell. Additionally, whoami is useful in bash scripting to show who runs the script.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to use the whoami command with examples.

Prerequisites
- A system running Linux (this tutorial uses Ubuntu 22.04).
- Access to the command line/terminal.
whoami Command Syntax
The syntax for the whoami command is:
whoami [option]The command also runs without any options.
whoami Command Options
The whoami command comes with two options. The following table explains them:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
--help | Shows a help message and exits. |
--version | Shows the version information and exits. |
whoami Command Examples
There are several ways to use whoami. The examples below elaborate on the whoami command use cases.
Show Current User in Linux Using whoami
When running whoami without any options, the output shows the name of the currently logged-in user.
To test the command, enter:
whoami
The output prints the effective user name, which is the user account the system uses to check what actions are allowed.
Verify the Effective User with whoami
When you have multiple accounts, use whoami to verify the username after switching to a different account. Take the following steps:
1. Switch to another user with the su command:
su [account name]For example, switch to user1 with:
su user1
2. Run the whoami command to verify the effective user:

Since you executed the command as a different user, the terminal shows another username.
Check an Account for Sudo Permissions Using whoami
Use the whoami command to check if a user has sudo privileges. To do this, execute the command with sudo and provide the password:
sudo whoami
The sudo utility runs the command with superuser (root) privileges. The whoami command then shows the effective user, which is root in this example.
In case you don't have sudo privileges, the output looks like this:

Note: Learn how to create a sudo user on Ubuntu.
Confirm Which User is Running a Script Using Whoami
The whoami command in bash scripts shows which user is running the script. For example, use whoami to test if root is executing the script, and if so, print a warning message using the echo command.
Use a simple bash if statement to test this:
if [[ "$(whoami)" != 'root' ]]
then
echo "You are running this script as root user!"
fi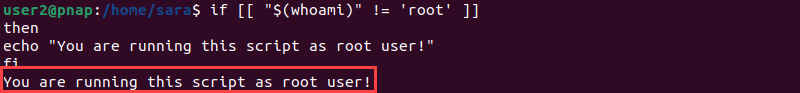
List All whoami Options
Execute the following command to show the help message for whoami and see all available options:
whoami --help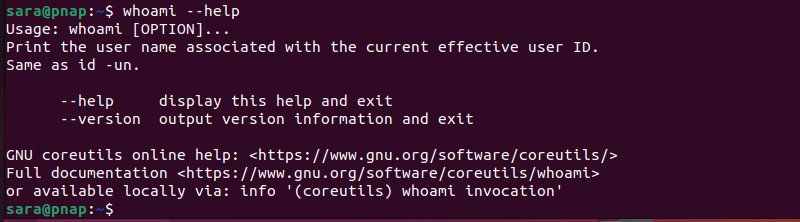
The output explains the whoami command usage. Furthermore, the terminal shows links to the online help page and the full documentation website.
To get even more information about the whoami command, use man whoami. The command opens the manual page for the whoami command, which provides detailed information, such as a description, usage, options, and examples.
Check whoami Version and Exit
To check the whoami command version, execute:
whoami --version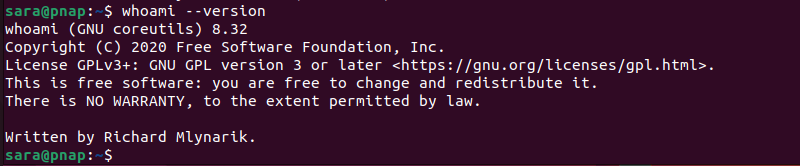
whoami vs. Other Commands
Some commands print the same output as whoami. The command descriptions are in the following table:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
w | Displays information about the users currently logged into the system and their processes. |
logname | Outputs the login name of the current user. |
who | Shows a list of users currently logged into the system. |
id | Prints user identity information, including user ID, group ID, and group memberships. |
The examples below explain the whoami alternatives.
whoami vs. w
While whoami only prints the username of the effective user, the w command provides more details. That is, the w command shows where users are logged in from and what they are currently doing.
w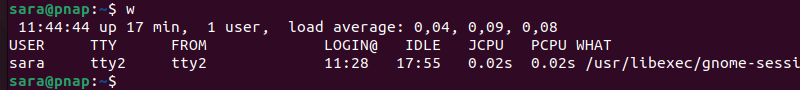
whoami vs. logname
Both whoami and logname show the name of the current user.
whoamilogname
The difference is that while the whoami command shows the effective user, the logname command only returns the username.
Test this by running the commands with sudo:
sudo whoamisudo logname
When using sudo with logname, the command returns the name of the current user. However, if you execute sudo with whoami, the command returns root.
whoami vs. who
The who command returns info about all logged-in users (not only the effective users). The command lists usernames, their terminal lines, and the times they logged in.
who
whoami vs. id
When executing the id command without any options, it returns the currently logged-in user details, like the user ID, the group ID, and the list of groups the user is in.
id
However, if you execute the id command with the -un option, the output is the same as with whoami.
id -unwhoami
Conclusion
This tutorial explained how to use the whoami command to find the name of the effective user on a Linux system.
For more information about Linux commands, check out and download this helpful Linux commands cheat sheet or refer to our in-depth list of basic Linux commands.