Python is an excellent programming language for manipulating textual data. Since Python treats strings as a character array, string slicing is a technique in Python that allows extracting substrings, which is handy when working with long strings.
This article shows different ways to slice a string and some valuable tricks when working with slicing.

Prerequisites
- Python 3 installed.
- A text editor or IDE to write the code.
- A terminal or IDE to run the code.
Python Slicing Methods
Python offers two ways to slice strings:
- The
slice()method splits the array according to the provided range parameters. - The array slicing notation performs the same task as the
<strong>slice()</strong>method, but uses different notation.
In both cases, the returned value is a character range. Every string behaves as a character array whose elements are accessible through indexes. There are two ways to access array elements in Python:
- Normal indexing accesses characters from the first to the last (starting at 0).
- Negative indexing accesses characters in reverse order (starting at -1).
Below is a detailed explanation of both methods and how they behave.
Method 1: Using slice()
Python's slice() method is a built-in function for extracting a specific string part. The method works on any array-like object, such as a string, list, or tuple.
The syntax is:
slice(start,stop,step)The arguments are indices with the following behavior:
- The
startvalue is the index of the first character in the subsequence. The default value is0orNone. - The
stopvalue is the index of the first character not included in the sequence. The default value isNone. - The final
stepvalue is the number of characters to skip between thestartandstopindices. The default value is1orNone.
The method returns an object containing the substring character array.
Use the slice() method to do the following:
- Extract a portion of a string with a step. Provide the
start,stop, andstepvalues like in the following example code:
quote = "There's no place like home."
print(quote[slice(0,-1,2)])
The method extracts every other character from the beginning up to (but not including) the last character.
- Define a range for a substring. Use two values to do so:
quote = "There's no place like home."
print(quote[slice(5,10)])
The slice() method fetches a substring from index five to ten, while the step value defaults to 1.
- Cut off a string at a particular index. Provide a single value, which represents the final index:
quote = "There's no place like home."
print(quote[slice(5)])
print(quote[slice(-5)])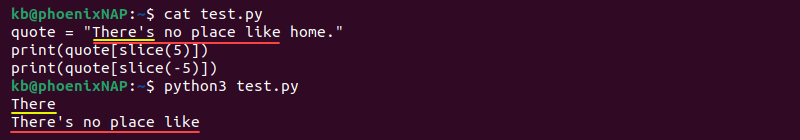
Positive indexing shows the first five characters, while negative indexing shows up to the last five.
- Reverse a string by using a negative
stepvalue. For example:
quote = "There's no place like home."
print(quote[slice(None,None,-1)])
The start and stop fields use default values because of the None parameter, while the step value is -1. The code reads the string backward and reverses the character order.
Method 2: Using Array Slicing [::]
Python uses the array slicing syntax to perform string slicing differently. Array slicing calls the slice() method and performs the same task. However, the syntax is more flexible. Instead of writing None for unstated indices, the field is blank to indicate default values.
Note: Think of array slicing as a range. A single index fetches the character at the provided index, while a range slices the string according to the stated range.
The syntax for array slicing is:
string[start:stop:step]Use array slicing to perform the following tasks:
- Extract a substring with a step from a string. Provide all three values like in the following example:
quote = "There's no place like home."
print(quote[3:-1:2])
The slicing starts the substring at the fourth character and goes to the end, printing every other character.
- Extract a substring from a string. Use the
startandstopvalues to define the range. For example:
quote = "There's no place like home."
print(quote[3:10])
The code fetches a substring starting at index three up to index ten. The step value defaults to 1 when left out.
- Print the last characters of a string. Leave any field blank to use default values. For example:
quote = "There's no place like home."
print(quote[-5:])
The slicing starts at the fifth to the last character and goes to the end. The step value defaults to 1 when left out.
Note: Learn how to merge two or more strings by referring to our guide How to Append a String in Python.
Conclusion
After going through the examples in this guide, you know how to slice a string. By providing a start, stop, and step value, string slicing allows extracting various values from the character array.
Slicing is a valuable tool for Python programmers working with string data types.
Next, learn how to use list comprehension in Python.



