The sed (stream editor) utility is a line-oriented text parsing and transformation tool. The sed command uses a simple programming language and regular expressions to process text streams and files. The most used sed command feature is string substitution.
This guide shows how to use sed to find and replace strings through examples.

Prerequisites
- Access to the terminal.
- A text file (this guide provides an example.txt file).
- Basic terminal commands (refer to our free Linux commands cheat sheet).
sed Find and Replace Syntax
The syntax to find and replace text using the sed command depends on whether you use the BSD or GNU sed version.
GNU sed Find and Replace Syntax
GNU systems, commonly found in Linux distributions, include specific versions of various command-line tools, such as sed. To find and replace text using the sed command in GNU systems, run:
sed -i 's/<search regex>/<replacement>/g' <input file>The command consists of the following:
-i. Tells thesedcommand to write the results to a file instead of standard output.s. Indicates the substitute command./. The most common delimiter character. The command also accepts other characters as delimiters, which is useful when the string contains forward slashes.<search regex>. Represents the string or regular expression search parameter.<replacement>. Represents the replacement text.g. The global replacement flag, which replaces all occurrences of a string instead of just the first.<input file>. The file where the search-and-replace occurs.
The single quotes help avoid meta-character expansion in the shell.
BSD sed Find and Replace Syntax
The BSD sed version (which includes macOS) does not support case-insensitive matching in the same way as GNU sed.
If you need to replace content in a file and do not want to use in-place editing, the command looks like this:
sed 's/<search regex>/<replacement>/g' <input file> > <output file>This approach saves the modified content in <output file>, leaving <input file> unchanged.
If you do want to modify the file in place, BSD sed supports in-place editing with the -i option, but it requires an additional argument (such as -i '' to specify no backup file):
sed -i '' 's/<search regex>/<replacement>/g' <input file>This modifies <input file> directly and saves the changes.
Alternatively, install the GNU sed version on macOS with homebrew:
brew install gnu-sedRun the GNU sed command as follows:
gsed -i 's/<search regex>/<replacement>/g' <input file>Replace the sed command with gsed to follow the examples below in macOS.
sed Replace Examples
The examples from this guide use a sample file to replace strings. Create a sample text file in a text editor of your choice with:
nano example.txtAdd the following contents to the file:
foobarbazfoobarbaz
foo bar baz foo bar baz
Foo Bar Baz Foo Bar Baz
FOO BAR BAZ FOO BAR BAZ
/foo/bar/baz /foo/bar/baz
Use the file as input to test the examples below.
Replace First Matched String
Replace the first found instance of the word bar with linux in every line of a file with:
sed -i 's/bar/linux/' example.txtThe -i tag inserts the changes to the example.txt file. The command has no output. Check the file contents with the cat command:
cat example.txt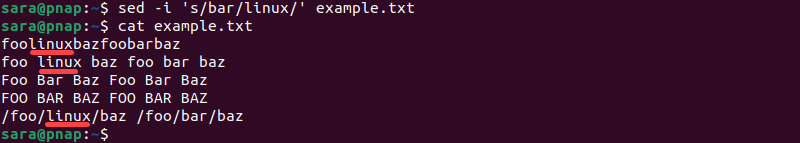
The command replaces the first instance of bar with linux in every line, including substrings. The match is exact and ignores capitalization variations.
Global Replace
To replace every string match in a file, add the g flag to the script. For example:
sed -i 's/bar/linux/g' example.txtCheck the outcome with cat:
cat example.txt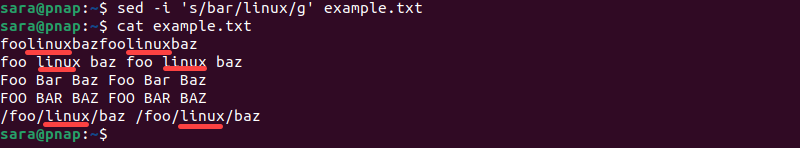
The command globally replaces every instance of bar with linux in the file.
Match and Replace All Cases
To find and replace all instances of a word and ignore capitalization, use the I parameter. Check the result with cat:
sed -i 's/bar/linux/gI' example.txtcat example.txt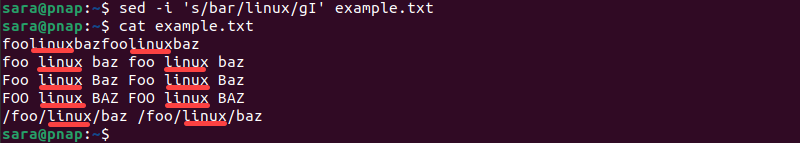
The command replaces all instances of the word bar in the text, ignoring capitalization.
Ignore Substrings
Add word boundaries (\b) to the sed command to ignore substrings when replacing strings in a file. For example:
sed -i 's/\bbar\b/linux/gI' example.txtThe command uses / as the delimiter between the search pattern and the replacement string. Alternatively, change the delimiter to : to make the command easier to read:
sed -i 's:\bbar\b:linux:gI' example.txtThe command ignores substrings, matching only the whole word. Verify the output with cat:
cat example.txt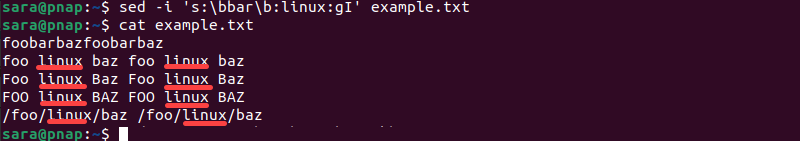
The result shows all instances of the standalone word bar have been replaced with linux, while substrings like foobar remain unchanged due to the word boundaries (\b).
Find and Replace with Regular Expressions
The search pattern for the sed command accepts regular expressions, similar to grep regex. For example, to match all capital letters and replace them with 5, use:
sed -i 's/[A-Z]/5/g' example.txtVerify the outcome with cat:
cat example.txt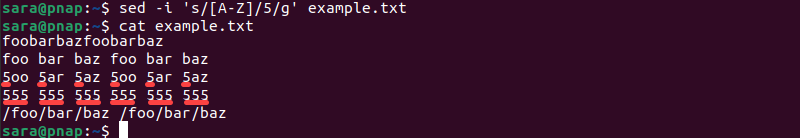
The regex pattern finds all capital letters and replaces them with the corresponding number in the file.
Reference Found String
Use the ampersand character (&) to reference the found string. For example, to add a forward slash (/) before every instance of foo in a file, use the following command and verify with cat:
sed -i 's/foo/\/&/gI' example.txtcat example.txt
Instead of retyping the search parameter, the & sign references the found string.
Create a Backup
To create a backup file before overwriting the existing one, add the .bak parameter to the -i tag.
sed -i.bak 's/foo/FOO/g' example.txtThe command replaces all occurrences of the word <strong>foo</strong> with FOO and creates a backup of the original file with a .bak extension. Verify the content of the changed original file with:
cat example.txt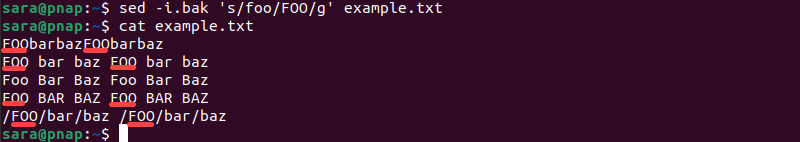
Confirm the content of the unchanged backup file with:
cat example.txt.bak
The command creates a backup, example.txt.bak, before overwriting the original. Use this method to keep a copy in the original format and avoid overwriting.
Recursive Find and Replace
Use the find command to search for files and combine it with sed to replace strings in files recursively. For example:
find -name 'example*' -exec sed -i 's/[a-z]/5/gI' {} +Verify the changes in example.txt and example.txt.bak files with:
cat example.txtcat example.txt.bak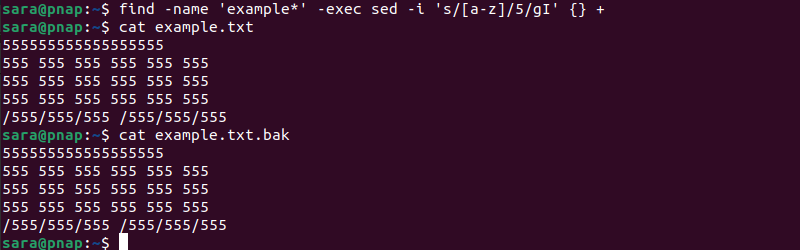
The command finds all files starting with example and executes the sed command on the files. The executed command replaces all letters with 5, ignoring capitalization.
sed Find & Replace: Problems with Default Delimiter Character
In sed, the default delimiter for the s (substitute) command is the forward-slash (/). However, this causes problems when the search or replacement text contains slashes, making the command difficult to read. This is common when working with file paths or URLs.
In that case, each slash in the search or replacement text must be escaped with a backslash to avoid confusing sed.
For example, file.txt contains the following line:
cat file.txt
To replace /home/user/old with /home/user/new in a file, using / as the delimiter requires escaping each / in the path:
sed 's/\/home\/user\/old/\/home\/user\/new/g' file.txtThis command works but is hard to read because of all the escaped slashes.
To solve this issue, choose a different delimiter, such as :. By changing the delimiter to :, you don't need to escape the slashes. Run the following:
sed -i 's:/home/user/old:/home/user/new:g' file.txtVerify the output with:
cat file.txt
Using Shell Variables with sed to Replace Text or Data
Use shell variables with sed to replace text or data dynamically. This is useful when you want to substitute values in a file based on variables, such as paths or strings defined in the shell.
To pass shell variables into sed, reference them inside the command with double quotes (") around the sed expression. Single quotes (') prevent variable expansion.
For example, replace foo with the value of a shell variable in example.txt. Take the following steps:
1. Define a variable with the following:
word_to_replace="foo"
replacement="FOO"2. Use the variable in the sed command
sed -i "s/$word_to_replace/$replacement/g" example.txtThe command consists of:
$word_to_replace. The shell variable that holds the word or string to be replaced (in this case,foo).$replacement. The shell variable that holds the word or string to replace the original with (in this case,FOO).
The sed command replaces all occurrences of foo with FOO in example.txt.
3. Verify the change with:
cat example.txt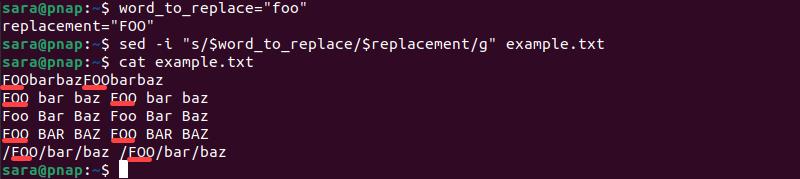
Conclusion
After going through the examples in this guide, you know how to use sed to replace strings in files. The sed command is a powerful text manipulation utility with many advanced features.
Next, learn how to use sed to delete a line from a text file or check out the awk or gawk command to learn about other text manipulation tools.