Docker Compose is a tool used to define and run multi-container Docker applications. Users utilize this software to launch, execute, communicate, and close containers with a single coordinated command.
This tutorial will show you how to install Docker Compose on CentOS 7.
Prerequisites
- A system running CentOS 7
- A user account with sudo privileges
- An existing Docker installation on CentOS
- A command-line/terminal window (Ctrl-Alt-F2)
Installing Docker Compose from GitHub Repository
You can download Docker Composer from the official CentOS repository, but it is generally not advisable to do so. The best option is to install the binary package from the GitHub repository as is it ensures you are downloading the most up-to-date software.
Following these simple steps to start using Docker Compose on CentOS.
Step 1: Update Repositories and Packages
Before starting any installation, make sure to update the software repositories and software packages.
In the terminal enter the following commands:
sudo yum updatesudo yum upgradeIn the next step, you will use the curl command to download the binaries for Docker Compose. Beforehand, check whether you have the required command-tool by typing:
curlcurl is installed on the system if the output displays the message curl: try 'curl --help' or 'curl --manual' for more information.

If you see curl: command not found, you will need to install it before setting up Docker Compose.
To install curl, use the command:
sudo yum install curlNote: For more tutorials on curl, visit our guides How To Set Or Change User Agent With Curl and How To Make Curl Ignore Certificate Errors.
Step 2: Download Docker Compose
First, download the current stable release of Docker Compose (1.24.1.) by running the curl command:
sudo curl -L "https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.24.1/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m)" -o /usr/local/bin/docker-composeThe –L option tells the system to follow any redirects, in case the file has been moved. –o changes the filename to docker-compose so you can easily find it when needed. The option /usr/local/bin/ specifies the location in which to store the software package.
Note: At the time of writing, the latest stable release of Docker Container was 1.24.1. To check for new releases, refer to the Docker Compose page on GitHub. To install a specific version, substitute 1.24.1 from the URL with the preferred version number.
Next, change the file permissions to make the software executable:
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-composeDocker Compose does not require running an installation script. As soon as you download the software, it will be ready to use.
Step 3: Verify Installation
To verify the installation, use the following command that checks the version installed:
docker–compose –-version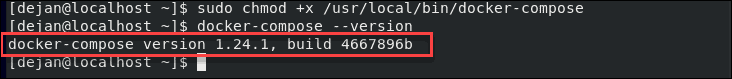
Install Docker Compose using Pip
If you are having trouble installing Docker Compose with the steps mentioned above, try downloading the software using the Pip package manager.
Simply type in the following command in the terminal window:
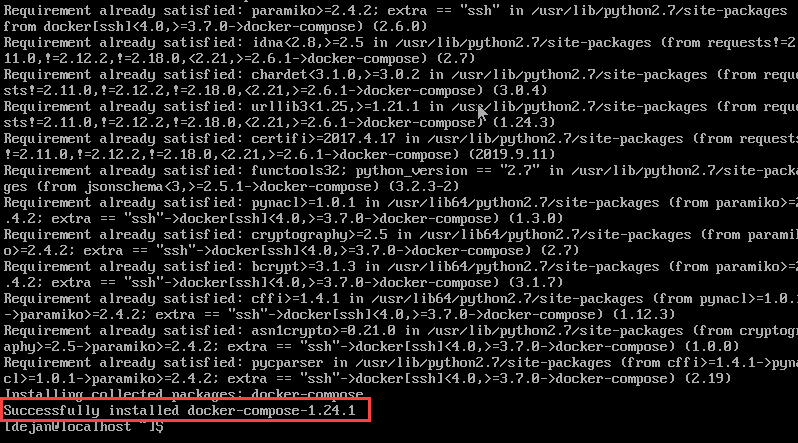
sudo pip install docker-compose
The output should show you if docker-compose-1.24.1 (the latest version at the time of writing) has been successfully installed.
Note: If you do not have Pip, take a look at our guide on How to Install Pip on CentOS.
How to Uninstall Docker Compose
To uninstall Docker Compose, if you installed using curl run:
sudo rm /usr/local/bin/docker-composeIf you installed the software using the pip command, remove Docker Compose with the command:
pip uninstall docker-composeConclusion
Now you know how to install Docker Compose on CentOS 7. The article includes two options for installation, one of which should work on your system.
After installation, you may want to look into the best practices for Docker container Management.