Docker allows users to run various applications isolated from the host computer, without the necessity of having separate operating systems for them to run on. Instead, you install and manage Docker containers with a containerization engine (Docker daemon), which has a similar role as the hypervisor for virtual machines.
As you start using Docker, you will face situations where you need to know how to share data between containers.
Prerequisites
- A user with sudo privileges
- Access to a terminal/command line
- A stable release of Docker
Step 1: Create a Container with Data Volume
To demonstrate how to share between two containers you need to create a container (Container1) with data volume (datavolume1) you can later share.
1. First, create an independent volume which you will share between two Docker containers:
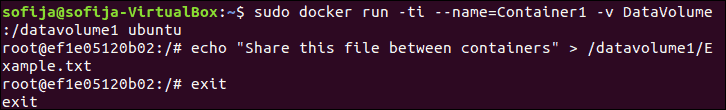
docker volume create --name DataVolume12. Then, create a Docker container and name it Container1 with data volume attached to it by running the following command:
docker run -ti --name=Container1 -v DataVolume1:/datavolume1 ubuntu2. Next, create a file in the data volume and add some text to it:
echo "Share this file between containers" > /datavolume1/Example.txt3. Exit the container with the command: exit
Step 2: Create a New Container and Add to the Data Volume
Next, create a new container (Container2) which will share files with Container1.
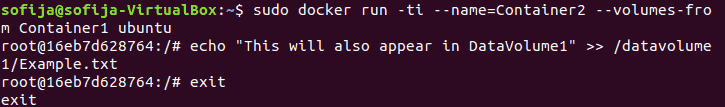
1. Create Container2 and mount the volumes from Container1:
docker run -ti --name=Container2 --volumes-from Container1 ubuntu2. Add text from Container2 to show that both containers can write to DataVolume1:
echo "This will also appear in DataVolume1" >> /datavolume1/Example.txt3. To exit from Container2 use the command: exit
Step 3: Verify You Can Share Data Between Docker Containers
1. Restart Container1 to check the changes to the data volume:
docker restart Container12. Confirm that both containers can read and write to the same data volume and that the text you wrote in Container2 appears in DataVolume1:
cat /datavolume1/Example.txtIf the text was successfully added to the data volume, the output should display the following:
Share this file between containersThis will also appear in DataVolume1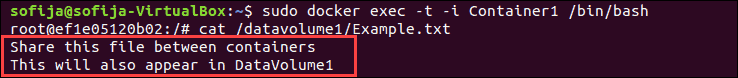
3. To finish, exit out of the container with the command: exit
Optional: Create Read-Only Volumes
Creating a “read-only” Docker container prevents others from making any changes to the data, allowing them only to view the files.
Add :ro to the container name which should be shared but not modified.
In the following example, Container2 will be allowed to see files from Container1 but will not be able to edit them.
docker run -ti --name=Container2 --volumes-from Container1:ro ubuntuTo check if Container2 has read-only privileges, try to remove the example file from Container1 by running the command:
rm /datavolume1/Example.txtThe output should show you have successfully created a read-only file. Consequently, other containers can access and view the data, but cannot make any contribution nor changes to it.

Conclusion
Now you know how to share files between Docker containers.
Also, this tutorial explained how to lock your files in Docker containers so that other parties cannot edit or remove them.