A hostname is a unique label assigned to a device on a network. The primary purpose of a hostname is to enable a device to identify itself to other network hosts.
This article shows how to set or change a hostname in CentOS and Rocky Linux.
Prerequisites
- System running CentOS or Rocky Linux.
- Command-line access.
- A user with sudo privileges.
How to Change CentOS and Rocky Linux Hostname
There are three types of hostnames on Linux:
- Static hostname. The primary hostname used by servers to identify another server.
- Pretty hostname. This hostname type allows for more characters and punctuation. However, since it uses non-standard characters, the machines cannot read it. Its purpose is to provide users with easy-to-read system IDs.
- Transient hostname. A temporary name that a device on a network receives from network configuration services such as DHCP and mDNS. It usually resets after a system reboot.
The following sections explain how to set and modify all three hostname types.
Set Static Hostname via CLI
CentOS and Rocky Linux only allow Fully Qualified Domain Names (FQDNs) to act as hostnames. An FQDN must:
- Have between two and 63 characters.
- Consist of lowercase letters (a-z), numbers (0-9), and symbols ('.' and '-').
- Start and end with a lowercase letter or a number.
Set a new hostname by typing the following command in the terminal, replacing [hostname] with a valid string of your choice:
hostnamectl set-hostname [hostname]For example:
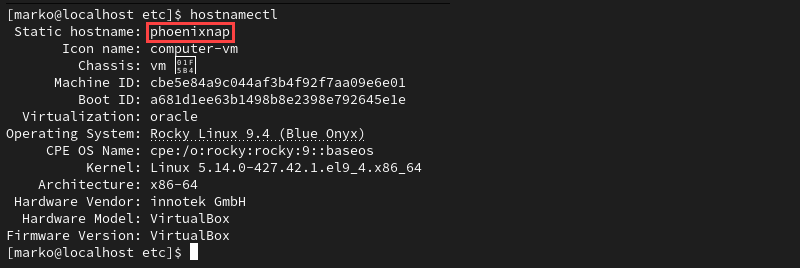
hostnamectl set-hostname phoenixnapThe command provides no output. To verify the hostname, use the following command:
hostnameThe output shows the currently set hostname.

Alternatively, execute the hostnamectl command without any arguments:
hostnamectlThe output displays the static hostname and other network configuration and operating system information.
Set Static Hostname by Editing /etc/hosts File
While the hostnamectl command is the recommended method to change the hostname on CentOS and Rocky Linux. It is also possible to perform this action by editing the system's hosts file. Follow the steps below to change the hostname in the hosts file:
1. Open the file in a text editor such as Nano:
sudo nano /etc/hosts2. Look for the line that begins with 127.0.0.1 (the IP address that refers to the system you are working on). The line contains the reference to the current hostname in the following format:
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost 4 localhost4.localdomain4 [hostname]3. Change [hostname] to a new hostname.
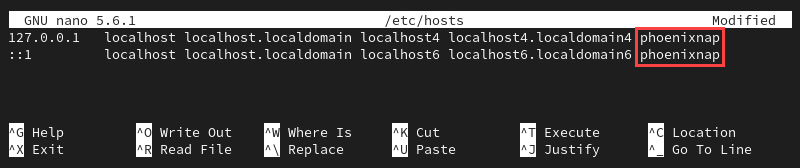
4. Save the file and exit.
5. Restart the system.
Set Static Hostname with nmtui
nmtui is a terminal user interface (TUI) program for network management that can set and modify the system's hostname. Proceed with the steps below to change the hostname using nmtui:
1. Launch nmtui by entering:
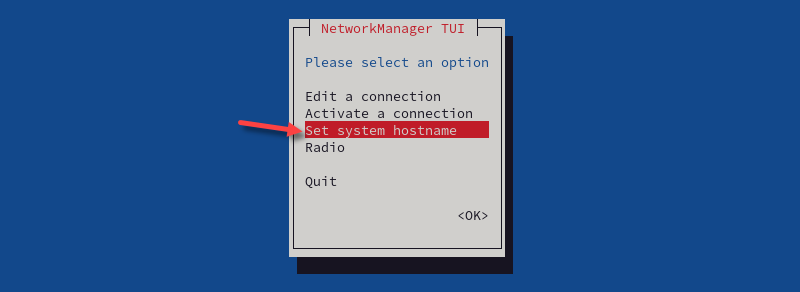
nmtui2. Use arrows to select the Set system hostname option, then press Enter.
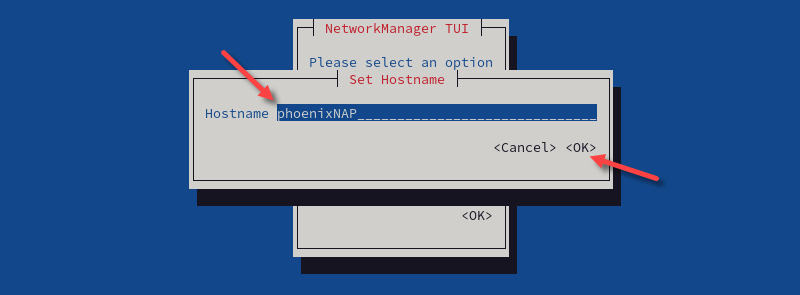
3. Type the new hostname in the Hostname text field, then select OK.
4. Use administrative credentials to authenticate and confirm the hostname change.
Set Pretty Hostname
The hostnamectl command can also set pretty hostnames in CentOS and Rocky Linux. Use the following syntax to set a pretty hostname on the system:
hostnamectl set-hostname "[pretty_hostname]"For example:
hostnamectl set-hostname "phoenixNAP's server"The system treats the complex characters within quotes as a pretty hostname. It also removes non-FQDN characters and uses the remaining characters to form the static hostname.
Checking the hostname info confirms the changes:
hostnamectl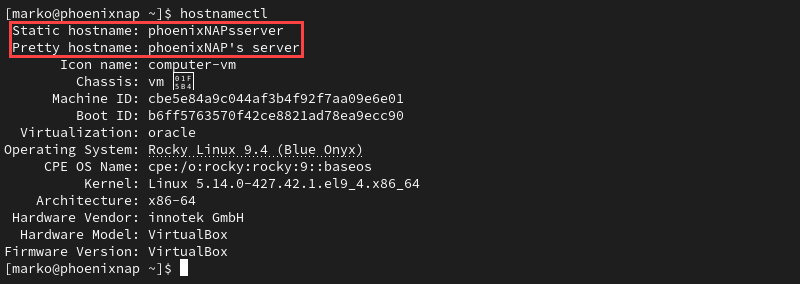
To set a pretty hostname only, i.e., without changing the static hostname, add the --pretty option to the hostnamectl command:
hostnamectl --pretty set-hostname "[pretty_hostname]"Set Transient Hostname
Set a transient hostname by using the --transient option:
sudo hostnamectl --transient set-hostname [hostname]Note: The transient hostname is not used if a static hostname is already set on the system.
The change lasts until the first reboot.
Conclusion
After reading this tutorial, you know how to change the hostname on your CentOS and Rocky Linux systems. The article covered different ways to set the static hostname and described the procedure for changing pretty and transient hostnames.
If you are new to Linux networking, read how to find your IP address in Linux.