Changing the speed and duplex settings of an Ethernet card in Linux can help optimize network performance, resolve connectivity issues, and define how effectively your servers communicate. The ethtool command allows you to configure these parameters easily to match the network environment.
This article will show you how to change the speed, duplex, and auto-negotiation settings in Linux with the ethtool command.

Prerequisites
- A user account with root privileges.
- Access to the terminal.
- The
ethtoolconfiguration tool installed.
How to Use ethtool Command to Set Speed & Duplex of Ethernet Card
The Linux ethtool command allows you to view and modify network device settings, including the speed, duplex mode, auto-negotiation, and driver information. Administrators can use the command to optimize and troubleshoot network interfaces by displaying statistics and performing tests.
The tool is especially useful for diagnosing network performance issues, configuring network parameters on the go, and ensuring that interfaces operate as expected. It is especially valued in environments where network reliability and performance are critical.
ethtool Command Syntax
The basic syntax for the ethtool command is:
ethtool [OPTIONS] [DEVICE][OPTIONS]- Flags and arguments to view or modify network settings.[DEVICE]- The name of the network interface you want to configure (for exampleeth0,enp0s3).
The most commonly used ethtool options are:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-s | Change the network settings for the specified device. |
-a | View the pause (flow control) parameters of the network interface. |
-c | Display interrupt coalescing settings (used to optimize packet handling). |
-g | Display the ring buffer settings. |
-i | Show driver information for the specified device, including the driver and firmware versions. |
-k | Display the offload and other hardware settings. |
-S | Show the statistics for the network device and driver. |
-T | View time stamping settings. |
-d | View the register dump. |
-e | Display EEPROM information (useful for analyzing device details). |
Running the ethtool command without any options, followed by the network interface name, displays basic information about the specified network interface. It is a quick way to check the current configuration and operational status of a network interface.
For example:
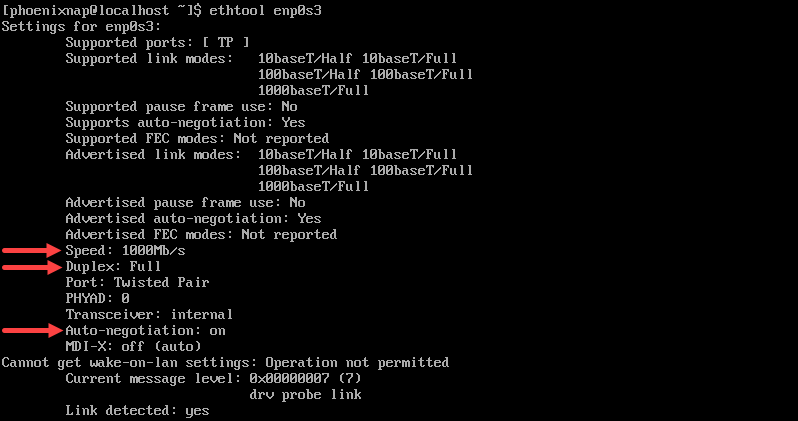
The output shows that the current speed is 1000Mb/s, that the Duplex is at Full, and that Auto-negotiation is turned on.
Note: Use the ifconfig command to find the name of your network device.
Use ethtool Command to Change Ethernet Adapter Settings
Use the ethtool command with the -s option to change the current ethernet adapter settings by defining the values for speed, duplex, and autoneg. The syntax for modifying the settings is:
sudo ethtool -s [device_name] autoneg [on/off] speed [10/100/1000] duplex [half/full]Note: The ethernet adapter settings cannot be changed for virtualized environments and on unsupported network drivers.
For example, to set the speed at 1000Mb/s, the duplex mode to full and the auto-negotiation to on for the enp0s3 device, the command is:
sudo ethtool -s enp0s3 autoneg on speed 1000 duplex fullConfirm that the changes have been applied by running the ethtool [device_name] command without options.
Use ethtool_opts Variable to Permanently Set ethtool Command Settings
By default, the system reverts the changes made with ethtool after a system reboot. Follow the steps below to utilize the ethtool_opts variable to apply custom settings each time a system boots:
1. Use a text editor to edit the ifcfg network configuration file for the device whose settings you want to change. For example:
sudo vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp0s32. Add the desired values as a line at the end of the file using the following syntax:
ETHTOOL_OPTS="speed [100|1000|10000] duplex [half|full] autoneg [on|off]"For example:
ETHTOOL_OPTS="speed 1000 duplex full autoneg on"3. Save the changes and exit the file.
After saving the file, the system applies the changes after every reboot, making them permanent.
Half Duplex, Full Duplex, and Auto-Negotiation
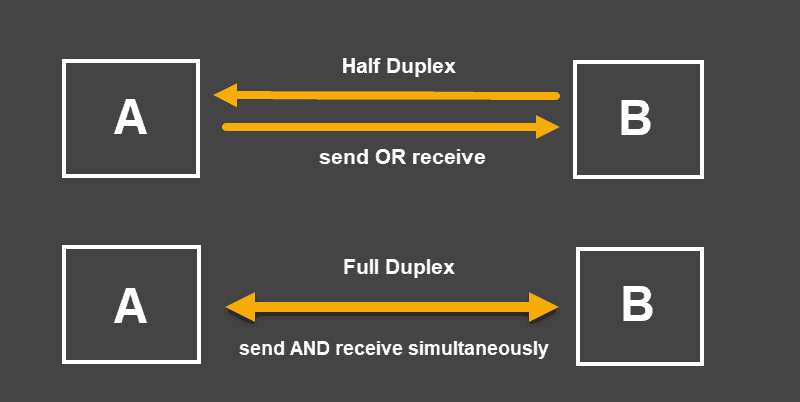
Half duplex mode allows a device to either send or receive packets in turn. A device set to this mode cannot perform both actions simultaneously.
When a device is in full duplex mode, it can send and receive packets simultaneously.
Auto-negotiation is a mechanism that allows a device to automatically choose the best-performing transmission mode based on its counterparts' characteristics. It is recommended to keep auto-negotiation enabled as it allows devices to choose the most efficient means for data transfer.
What Is a Duplex Mismatch?
When a device with enabled auto-negotiation connects to a device not using this signaling method, the operation fails. The device with active auto-negotiation can detect the other device's speed but cannot correctly detect the duplex mode. As a rule, the auto-negotiating end of the connection will use half-duplex while the other end might be at full-duplex. This situation is considered a duplex mismatch.
A duplex mismatch does not stop communication completely. Single packets and small amounts of data do not cause immediate issues. However, the connection speed drops significantly when a large amount of data is sent from either end. The connection works, but the performance is reduced as the data transfer rate is asymmetrical and might lead to packet loss.
Conclusion
This tutorial showed how to change the settings on your Network Interface Card using the ethtool command. You should now also have a better understanding of how auto-negotiation and duplex modes affect device performance.
Next, learn about the Linux ip command, a useful network interface tool, or learn more about Linux commands and download a handy cheat sheet.