InnoDB is the preferred storage engine for MySQL tables. MyISAM lacks many advanced features required for modern database systems.
Database administrators and developers convert table storage engines from MyISAM to InnoDB to gain these benefits, such as ACID compliance, foreign key constraints, and robust crash recovery mechanisms.
This guide shows how to check a database table's current storage engine and how to convert it from MyISAM to InnoDB.
Prerequisites
- Backup of the database. See our guide on how to back up and restore a MySQL database.
- Access to the command line or phpMyAdmin.
- A MySQL user account with root privileges. Learn how to check user privileges in MySQL and how to create a MySQL account and grant privileges.
- MySQL version with InnoDB support (use the
SHOW ENGINES;command to check).
How to Check Current Storage Engine
There are several ways to check the current storage engine for a MySQL table. Depending on the local setup, choose a method that best suits your environment and follow the steps in the sections below.
Note: We recommend using InnoDB instead of MyISAM to improve MySQL performance. Learn why by reading our in-depth comparison: MyISAM vs. InnoDB.
Check Current Storage Engine via Command Line
To see the default storage engine for a MySQL database table via the command line, do the following:
1. Connect to the MySQL shell via the terminal:
mysql -u [username] -pReplace [username] with the actual username.
2. Enter the user's password when prompted.
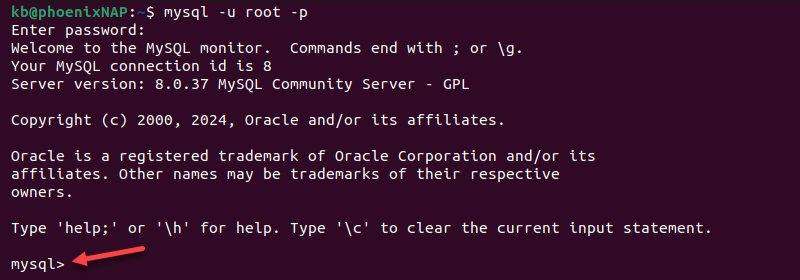
The command line changes to the MySQL shell prompt.
3. Use the following command to display information about a table and its storage engine:
SHOW CREATE TABLE [database_name].[table_name]/G;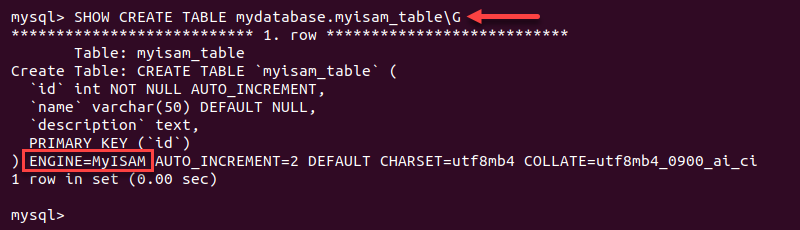
The ENGINE field shows the table's storage engine.
Note: Not sure what the database name is? See how to list all databases in MySQL.
4. To view the storage engine for all tables in a database, use the following query:
SELECT table_name, engine
FROM information_schema.tables
WHERE table_schema = '[database_name]';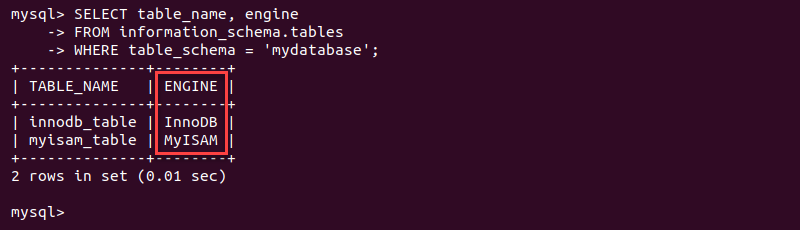
The SELECT statement shows table names in the first column and the engine for each table in the second column.
Check Current Storage Engine via phpMyAdmin
There are two ways to check the default storage engine in phpMyAdmin:
- From a table list.
- By running a query.
The sections below demonstrate both methods.
Note: To install phpMyAdmin, check out our guides for different operating systems:
Check Storage Engine from a Table List
A table list can help you determine which tables use MyISAM or InnoDB as the default storage engine:
1. Open phpMyAdmin and log in using your credentials.
2. Select the preferred database from the left menu.
3. In the Table list, locate the Type column to see the types of storage engines. Alternatively, use the filter to refine the list.
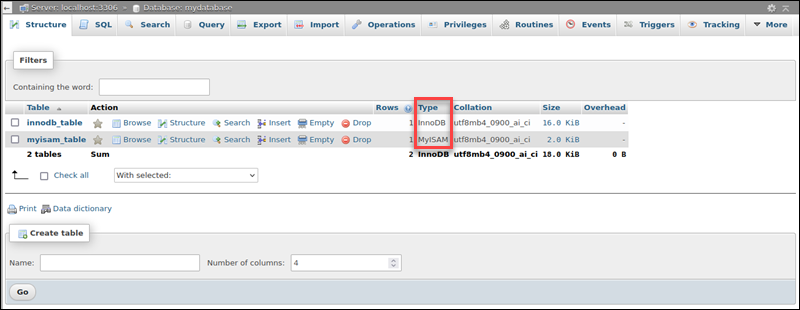
The column shows the storage engine type for every table.
Check Storage Engine with a Query
Another way to display a default storage engine is to run a query:
1. Log in to phpMyAdmin.
2. Select the preferred database from a database list.
3. Click the SQL tab to access query options.
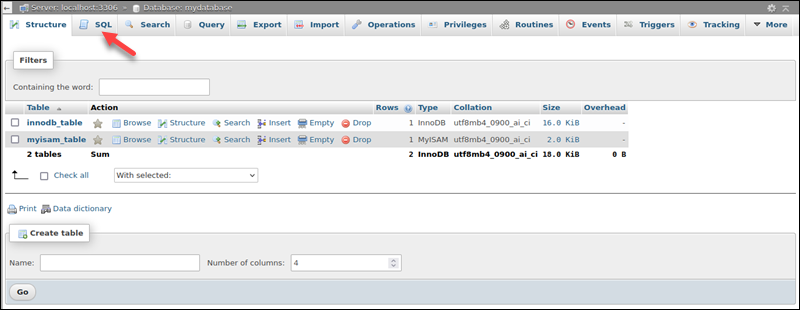
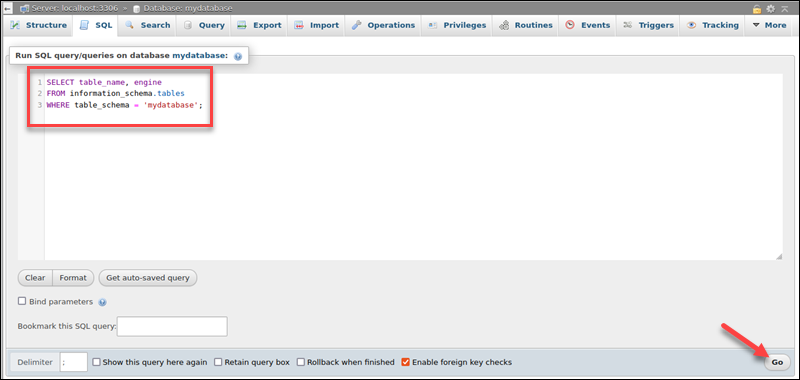
4. Enter the following query to display all tables and their storage engine:
SELECT table_name, engine
FROM information_schema.tables
WHERE table_schema = '[database_name]';Replace the [database_name] placeholder in the query with the database name.
5. Click Go to run the query.
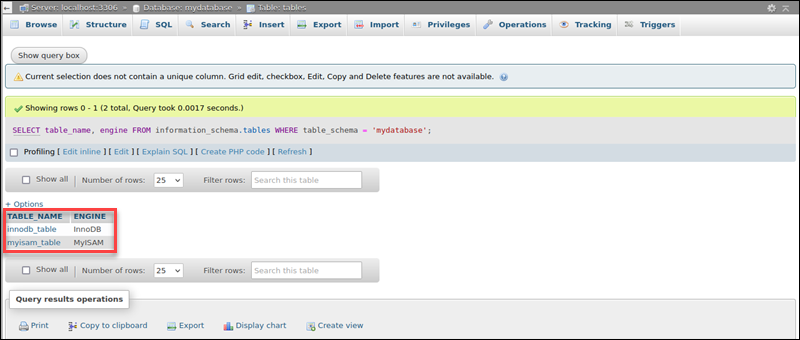
The result shows a list of all tables and their storage engine.
How to Convert MyISAM Tables to InnoDB
Converting a table from MyISAM to InnoDB (or the reverse) requires changing its storage engine. Two standard methods to accomplish this are through the command line or phpMyAdmin.
The sections below show how to convert a table using these two methods.
Convert MyISAM Tables to InnoDB via Command Line
Use the ALTER TABLE command in the MySQL shell to convert a table's storage engine from MyISAM to InnoDB and vice versa:
1. Connect to the MySQL shell:
mysql -u [username] -p2. Connect to the desired database:
USE [database_name];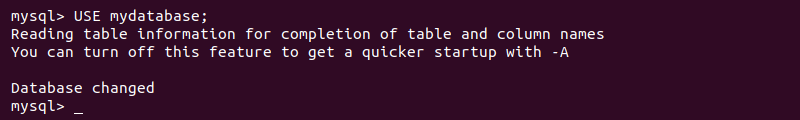
3. Run the ALTER TABLE query:
- To convert MyISAM to InnoDB, run:
ALTER TABLE [database_name].[table_name] ENGINE=InnoDB;- To revert InnoDB to MyISAM, run:
ALTER TABLE [database_name].[table_name] ENGINE=MyISAM;
The command shows a confirmation message.
4. Recheck the storage engine:
SHOW CREATE TABLE [database_name].[table_name]\G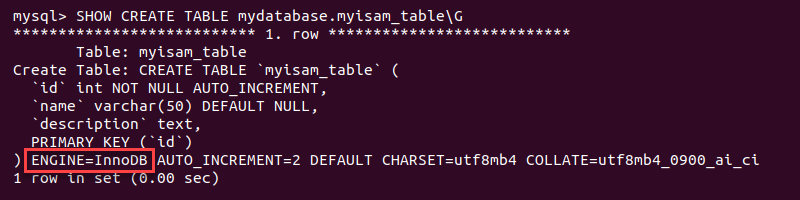
The query shows the storage engine changed, indicating the conversion was successful.
Convert MyISAM Tables to InnoDB via phpMyAdmin
There are two ways to convert the storage engine in phpMyAdmin:
- Using the Table Operations menu.
- Running a query.
The sections below explain both of these methods.
Convert using the Table Operations Menu
To convert a table using this method, do the following:
1. Log in to phpMyAdmin.
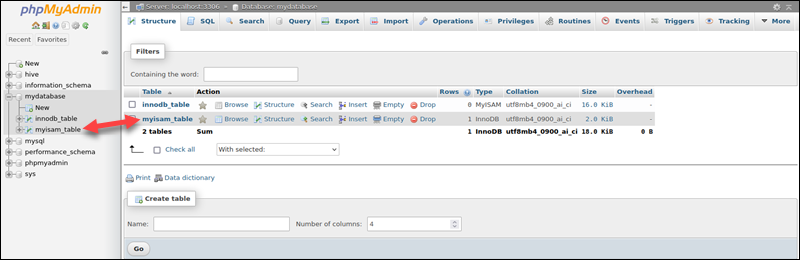
2. Select the preferred database from the left menu.
3. Click the table name for which you want to modify the storage engine from the left menu or the table list on the right.
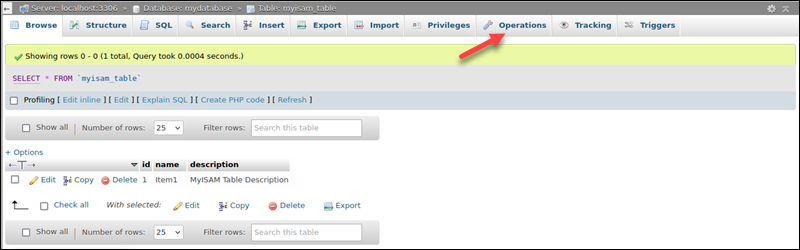
4. Click Operations to access the menu.
5. In the Table options section, locate the Storage engine drop-down menu. Open the menu and select InnoDB from the list.
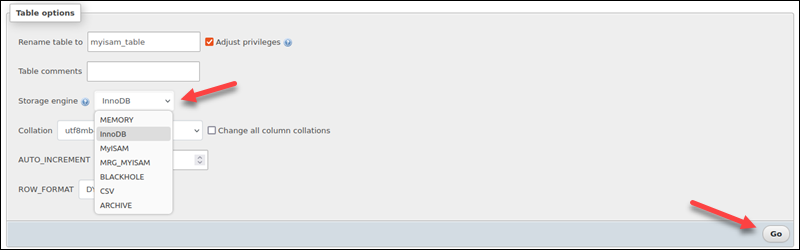
6. Click GO to apply the change and convert the table.
Convert with a Query
To convert a table using a query, follow these steps:
1. Log in to phpMyAdmin.
2. Select the database in the left menu.
3. Open the SQL tab for the preferred database.
4. Run the ALTER TABLE command in the MySQL shell to convert the storage engine:
- To convert to InnoDB:
ALTER TABLE [table_name] ENGINE=InnoDB;- To revert to MyISAM:
ALTER TABLE [table_name] ENGINE=MyISAM;Replace [table_name] in the appropriate command.
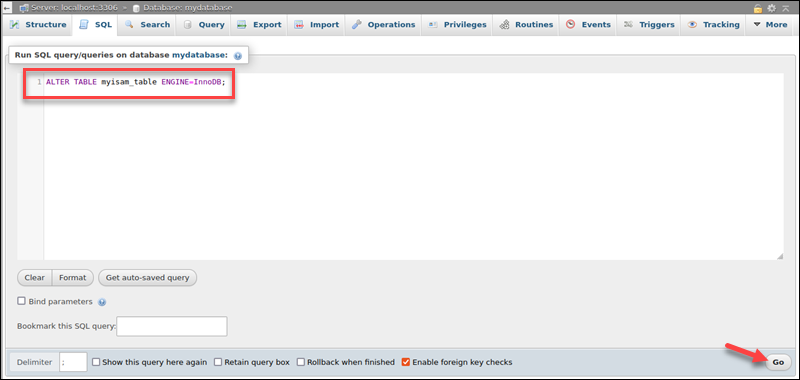
5. Click the GO button to run the query.
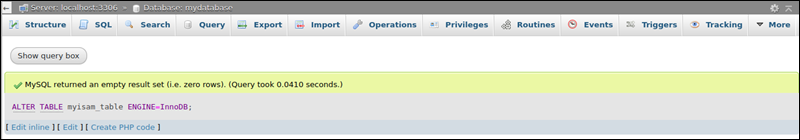
The query does not produce an output. Instead, a confirmation message affirms the modification is successful.
Conclusion
This guide showed how to convert a MySQL table storage engine from MyISAM to InnoDB (and vice versa). By following the steps in this guide, you have successfully converted a table's storage engine via the command line or phpMyAdmin.
Next, read more about how to optimize MySQL tables.