Over 72% of companies rely on some form of a hybrid cloud strategy. This tactic enables businesses to combine the cost-effectiveness and flexibility of public clouds with the tight control of on-prem infrastructure. However, success is far from guaranteed when deploying a hybrid environment.
Developing a hybrid cloud requires careful planning on how to deal with the complexities of integration, data management, and security within a hybrid environment. Without sufficient planning, these deployments often end up glitchy, unstable, and needlessly expensive.
This article presents a step-by-step guide to creating a well-rounded hybrid cloud strategy. Jump in to learn how to properly plan for this cloud deployment model, plus see the most common pitfalls when developing a hybrid cloud strategy.
Learn about hybrid cloud benefits and see why so many companies choose to host workloads in hybrid environments.
What Is a Hybrid Cloud Strategy?
A hybrid cloud strategy is a detailed plan for deploying an integrated IT environment that combines on-prem and cloud computing resources. Applications and data within this single, flexible infrastructure can migrate seamlessly between different IT environments.
The goal of a hybrid cloud strategy is to figure out the most effective and business-impactful way the adopter can combine the following IT components:
- On-site infrastructure that runs in the company's server room or data center.
- Multi-tenant public cloud infrastructure rented from a third-party cloud provider.
- Private cloud infrastructure dedicated solely to a single organization (on-premises or hosted at a third-party facility).
A hybrid cloud strategy is typically not a formal standalone document with a specific template or format. However, organizations often find it beneficial to document some aspects of their hybrid cloud strategy.
Companies typically outline major hybrid cloud considerations in their broader IT strategy plans. Other documents that adopters commonly create include:
- Usage policies that specify how and when teams should use different types of cloud services.
- Architecture guidelines for designing apps and systems compatible with the hybrid cloud environment.
- Guides that document specific security and compliance measures and requirements.
- Documents that outline the expected performance levels for each IT component and SLAs from each provider.
Hybrid cloud strategies require continuous optimization. The tech landscape evolves rapidly, so ongoing assessment and adjustments are crucial to ensuring the strategy remains effective and in line with business goals.
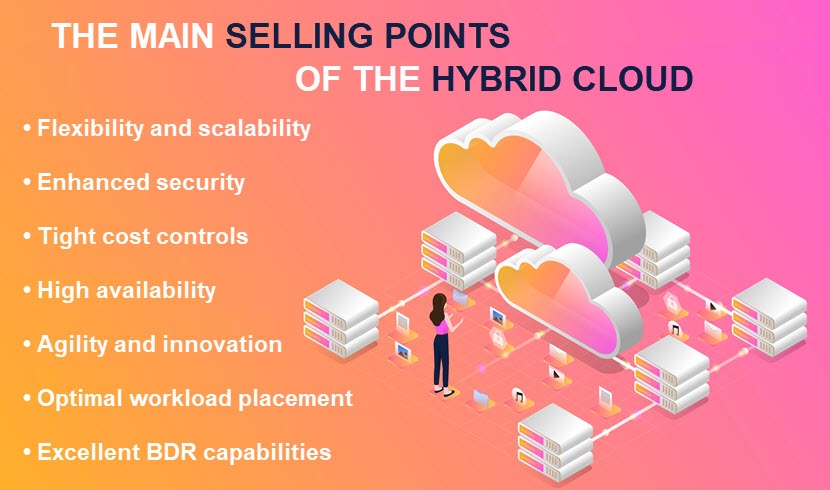
How to Build a Hybrid Cloud Strategy?
While every hybrid cloud adopter must contend with their own infrastructure and business needs, all successful adoption strategies follow a similar pattern. Follow the steps below to create an effective hybrid cloud strategy that aligns with your organizational goals, budget, and IT priorities.
Unsure about the DIY approach to hybrid cloud strategizing? Check out pNAP's hybrid cloud solutions and see how our team can help you plan and deploy a hybrid cloud environment.
Step 1: Set Objectives and Expectations
Defining objectives is a crucial initial step when creating a hybrid cloud strategy. Adopters must articulate the reasons for choosing a hybrid cloud over other models and outline the specific goals they aim to achieve with the deployment.
Start by identifying broader business goals and objectives that drive the need for a hybrid cloud. Many strategies have two or more business goals. Here are a few common objectives:
- Accelerate app development and deployment.
- Speed up performance.
- Improve customer experience.
- Enhance scalability.
- Reduce IT costs.
- Ensure compliance with an industry-specific regulation.
- Create a new or improve an existing disaster recovery (DR) strategy.
- Boost service availability.
Next, establish clear metrics you aim to achieve by implementing the hybrid cloud strategy. The usual key performance indicators (KPIs) for a hybrid cloud strategy are:
- Cost efficiency metrics, such as cost savings or ROI.
- Workload performance.
- Availability and uptime of apps and services.
- Resource utilization.
- Latency of data transfers between on-prem and cloud environments.
- Resource provisioning and de-provisioning times.
Adopters must also assess the financial aspects of their hybrid cloud strategy. Consider how much the organization can invest in its new cloud, plus analyze how a hybrid cloud will optimize costs compared to an all-on-prem or all-cloud solution.
Document the allocated budget and list all potential cost savings, cost avoidance, and factors that could impact the overall budget.
Another noteworthy consideration during this step is assessing whether the in-house team has the necessary know-how to set up and manage a hybrid cloud. Identify training needs and bridge any skill gaps that may slow down the adoption or hinder post-deployment operations.
Step 2: Assess Your Current IT
Assessing infrastructure provides the foundation for understanding your organization's existing IT capabilities, limitations, and potential areas for improvement. Make an in-depth inventory of existing IT assets by performing the following tasks:
- Conduct a comprehensive inventory of on-prem hardware, including servers, storage, and networking equipment. Assess the age, capacity, performance, and security requirements of each component.
- Document all on-site apps and their versions.
- Catalog data assets to understand where you store and how you access files.
- Document your network topology, including all your LANs, WANs, SD-WANs, and VPN connections. Evaluate current bandwidth usage and assess whether the infrastructure can support increased data transfers.
- Identify any third-party systems or services integrated with on-prem infrastructure.
- Map out dependencies between apps and services.
- Document all currently used security measures, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDSes), and access controls.
Create comprehensive documentation, as this analysis will be valuable in the later stages of the hybrid cloud implementation and ongoing management. Include configuration settings, network diagrams, and operational procedures, plus evaluate the TCO of existing infrastructure.
Here are a few other worthwhile tasks you should complete during this step:
- Analyze the current utilization of on-prem resources. This process helps identify potential bottlenecks or areas of underutilization you can address with your hybrid cloud strategy.
- Review existing governance policies and procedures. Consider how they must evolve to align with your hybrid cloud strategy.
- Conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify potential threats to your systems. Prioritize risks based on impact and likelihood.
- Run a vulnerability assessment to identify potential exploits in your current systems.
- Perform a business impact analysis (BIA) to understand your organization's critical functions and processes.
- Identify each critical function's maximum allowable downtime (RTO) and acceptable data loss (RPO).
Learn the difference between RTO and RPO, two closely related metrics that help ensure disruptions do not significantly impact your bottom line.
Step 3: Determine Workload Placements
Your next task is to determine which workloads are best suited for the public cloud, which should remain on-prem, and which ones belong in a private cloud. Start by categorizing existing workloads based on the following factors:
- Overall criticality to operations.
- Computational intensity.
- Performance requirements.
- Dependencies.
- Data sensitivity.
Remember to account for any seasonal or periodic spikes in demand that affect workload scalability requirements. Next, perform the following tasks for each workload:
- Define performance benchmarks, availability, response times, data transfer patterns, and latency tolerances.
- Specify how workloads must scale to accommodate the required loads.
- Detail security and compliance requirements for each workload.
Determine the optimal placement in the hybrid cloud architecture for each workload. Some workloads perform best on-prem, while others are a better fit for a public or private cloud. If you must pull existing workloads from a public cloud during this step, refer to our guide to cloud repatriation.
Once you identify which workloads you'll migrate to the cloud, determine the optimal way to handle the migration. There are two general options:
- Lift and shift. This approach involves moving workloads and apps to the cloud with minimal modifications. Lift and shift migrations are suitable for simple workloads with straightforward requirements.
- Refactoring or rearchitecting. This approach requires the team to modify the app's code, either moderately or extensively. The most common example is containerizing an app before moving it to the cloud. Refactoring is the go-to option for apps that benefit from cloud-native features.
Our article on cloud workload analysis explains how to effectively analyze current workloads and determine strategies for moving them to the cloud.
Step 4: Choose Cloud Services and Providers
Select the appropriate cloud service models for the workloads you plan to host in the public cloud. The three primary cloud service models are:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the Internet. This service allows users to rent virtual machines, storage, and cloud networking infrastructure on a pay-as-you-go basis.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS). PaaS delivers a cloud-based platform that includes a computing infrastructure and helpful development tools and services.
- Software as a Service (SaaS). SaaS delivers fully functional apps over the Internet, accessible over a web browser without local installations or maintenance.
A hybrid cloud strategy often involves a combination of these three services to meet different business requirements. Multiple service types allow an organization to leverage the benefits of each service model based on specific workloads and use cases.
Once you know what cloud services you require in your hybrid cloud, assess different cloud providers that meet your IT requirements. Pick a vendor (or multiple providers) based on factors such as:
- Offered SLAs.
- Security track record.
- Compliance guarantees.
- Reputation within your specific niche.
- Cloud costs.
- Built-in integrations.
- Compatibility with existing on-site systems.
Our comparison of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS provides an in-depth look at the main advantages and disadvantages of each cloud service model.
Step 5: Network Planning
Previous steps provided enough info to create a basic hybrid cloud architecture. Your next task is to decide how best to connect all the desired components.
Effective connectivity is crucial for achieving optimal performance, security, and reliability in a hybrid environment. Design a robust network architecture that enables secure and reliable connectivity between on-prem infrastructure and cloud services.
Usual go-to technologies for seamless integration include VPNs, cloud on-ramps, and dedicated interconnects. The main factors when choosing connectivity tech are:
- Types of workloads you plan to run.
- Your data transfer speed requirements.
- Security considerations.
- The allocated budget.
- Available in-house expertise.
Assess bandwidth requirements and latency considerations to evaluate optimal performance and data transfer speeds. Most hybrid environments have cloud bursting capabilities that allow an organization to seamlessly scale workloads from on-prem to the cloud during peak demand. Ensure your strategy maximizes this highly valued benefit of hybrid clouds.
Consider using load balancing to distribute incoming traffic across multiple servers or instances. Load balancing enhances scalability and ensures even distribution of workloads, both of which are vital to a hybrid cloud.
Step 6: Data Management and Storage Strategies
This step focuses on designing effective data management and storage strategies for your new IT environment. Proper data handling is pivotal for achieving efficiency, reliability, and compliance in your hybrid cloud strategy.
Classify your data based on sensitivity, regulatory requirements, and usage patterns. Identify which data should remain on-prem, what files will live in the public cloud, and what data shall reside in a private cloud.
Implement a data lifecycle management strategy that aligns with business requirements and relevant compliance standards. Here's what you should create during this stage:
- Data retention policies.
- Policies that regulate who has access to specific data and under what circumstances.
- Archival procedures.
- Data deletion protocols.
- Policies for sharing and collaborating on data.
Next, choose appropriate storage solutions for your hybrid environment. Leverage on-prem storage for sensitive data that requires local access while utilizing the cloud for scalable and cost-effective storage.
Utilize cloud-based object storage, file storage, or block storage solutions based on the specific workload requirements. Also, consider implementing data replication and synchronization mechanisms to ensure consistency across on-prem and cloud-based data sets.
You should also develop a backup strategy during this step, both for on-prem and cloud-based data. Key factors that drive decision-making during this process are backup frequency, retention policies, and data recovery objectives.
Check out pNAP's backup and restore services to see how we help companies create highly effective data backup strategies.
Step 7: Hybrid Cloud Security
The distributed nature of resources in a hybrid cloud makes security a vital consideration. The more security precautions and controls you implement, the better. Here's an overview of what you can add to your strategy to ensure sufficient cloud security:
- Develop and implement comprehensive security policies for both on-prem and cloud environments. The two must-haves are network and cloud security policies.
- Implement governance controls that define who has access to specific data types and under what conditions.
- Include strong IAM practices to control and monitor access to resources. Integrate IAM across on-prem and cloud environments to ensure consistent access controls.
- Use encryption for data both in transit and at rest. Outline key management best practices to ensure teams manage encryption keys securely.
- Secure communication between on-prem and cloud components using VPNs or dedicated connections.
- Use firewalls, IDSes, and network segmentation to protect against unauthorized access.
- Implement robust cloud monitoring to detect and respond to security incidents.
- Create an incident response plan that covers procedures for identifying, containing, and recovering from security incidents.
- Implement regular data backup practices with off-site storage to ensure data recovery in case of accidental deletion, corruption, or other incidents.
- Define a proactive patch management strategy to lower the chance of zero-day exploits.
Ensure your new hybrid cloud strategy complies with relevant industry regulations and standards (GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, etc.). Choose cloud regions that align with relevant regulations if you plan to host compliance-tied data in a public cloud.
Step 8: Cost Considerations
Cost optimization is a critical aspect of any hybrid cloud strategy. The team must continuously monitor resource utilization and right-size instances to match the actual needs of your workloads. Include automated alerts in your strategy to notify you when costs exceed preset thresholds.
Choose the appropriate storage class based on access frequency and performance requirements. Use cheaper instances for non-critical workloads that can tolerate interruptions. Explore serverless computing options for workloads with sporadic or unpredictable usage patterns.
Here are a few other worthwhile ideas to consider adding to your hybrid cloud strategy:
- Use auto-scaling features to dynamically adjust resources based on demand.
- Leverage reserved instances or savings plans offered by providers to commit to a certain amount of usage in exchange for discounted rates.
- Minimize data transfer costs by optimizing data flows and considering regional placement of resources.
- Implement content delivery networks (CDNs) to ensure cost-effective content distribution.
- Use lifecycle policies for storage to automatically transition data to lower-cost storage classes and delete outdated data.
- Use automated tools or scripts to periodically scan for idle resources. Decommission unused or underutilized resources to avoid unnecessary costs.
- Deploy cost monitoring tools to get detailed insights into resource costs.
Read our article on hybrid cloud costs to see how much you should expect to spend on an average hybrid cloud deployment.

Challenges of Building a Hybrid Cloud Strategy
Planning to set up a hybrid cloud comes with several notable challenges. The only way to reliably prevent these issues is to know about them in advance, so let's look at the most common challenges of devising a hybrid cloud strategy.
Learn about hybrid cloud challenges and see the most common problems adopters face when deploying and managing a hybrid cloud.
Integration Difficulties
A hybrid cloud requires seamless connections and coordination between on-prem and multiple cloud environments. Ensuring safe and efficient integration is a significant challenge.
Here are the main reasons why integration is such an issue in hybrid cloud strategies:
- Diverse technologies. On-prem and cloud environments use different technologies, protocols, and data formats. Integrating systems often leads to compatibility issues.
- Complex architecture. Defining how different components interact, share data, and communicate adds complexity to the integration process. Differences in APIs, service offerings, and underlying technologies often hinder seamless integration.
- App integrations. Ensuring an app seamlessly functions across on-prem and cloud environments is often difficult. Issues arise due to differences in operating systems, dependencies, or other app-specific factors.
- Data synchronization. Teams often struggle to ensure data is available and consistent between on-prem databases and cloud storage.
- Network connectivity. Addressing latency, bandwidth, and reliability concerns requires careful consideration of network architecture.
The only way to counter integration complexity issues is to invest sufficient time into planning your hybrid cloud strategy. Make use of standardized protocols and APIs, leverage middleware solutions, and consider the use of integration platforms. Experienced integration specialists, whether in-house or outsourced, also help navigate these challenges.
Security Risks
There are two primary reasons why security is a major challenge when devising a hybrid cloud strategy. Firstly, data in a hybrid cloud regularly moves between different IT environments. Continuous data movement creates various opportunities for cyber-attacks and breaches.
The most reliable way to keep data safe in a hybrid (or any other) environment is to invest in data encryption. Encryption at rest and in transit is non-optional, and many adopters also opt to set up encryption in use.
Robust access controls are also a must-have. Restricting access based on roles and responsibilities is another layer of defense against unauthorized access.
The second major security concern of hybrid clouds stems from the integrations between different IT environments. Tight integration between on-prem and cloud-based resources creates ample room for vulnerabilities.
Since points of contact between on-prem and cloud environments are potential attack vectors, any hybrid cloud strategy must focus on the following precautions:
- Securing APIs.
- Ensuring secure communication channels.
- Regularly auditing integration points.
Ensuring visibility across the entire infrastructure is vital. Include tried-and-tested tools into your strategy to ensure teams can monitor activities both in on-prem and cloud-based systems.
Check out the market's top cloud monitoring tools that help detect security-related events within cloud-based environments.
Data Management Challenges
A hybrid cloud strategy distributes data across on-prem infrastructure and two or more cloud platforms. Ensuring the integrity and accessibility of data across these diverse environments presents considerable challenges.
Here's an overview of what adopters do to ensure their hybrid cloud strategy has a sound plan for data management and consistency:
- Implement synchronization mechanisms that ensure updates and changes reflect uniformly across the hybrid environment.
- Use data integration tools with ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes that streamline data flows between on-prem and cloud systems.
- Utilize data replication mechanisms to create redundant copies of data for high availability and disaster recovery.
- Implement a versioning mechanism for data to help track changes over time.
- Use metadata management to track the lineage, quality, and usage of data across the environment.
- Define strict data lifecycle management policies.
- Develop effective data migration strategies to ensure integrity and validate successful migrations.
Adopters must continually assess their data management processes. Remember to adapt your hybrid cloud strategy to changing requirements and threats.
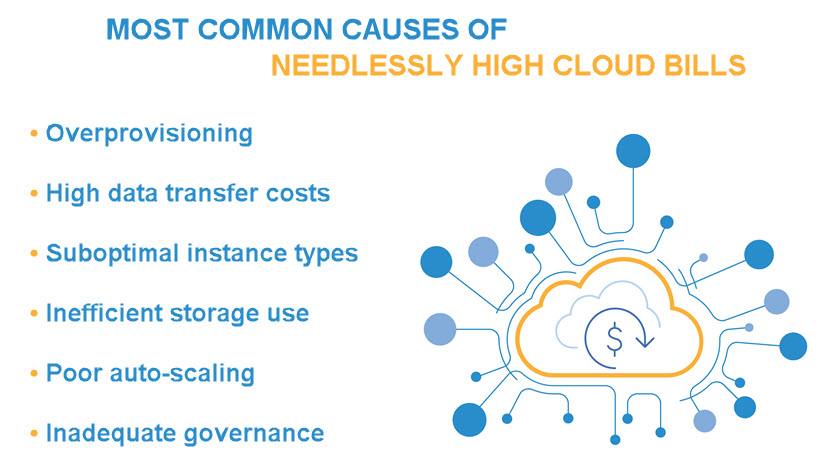
Planning for Post-Deployment Costs
Cost management and optimization are crucial considerations when devising a hybrid cloud strategy. The goal is to balance performance and flexibility without letting costs spiral out of control.
Staying within the allocated budget during deployment is less challenging than controlling post-setup costs. Here are a few cost-related precautions to consider adding to your hybrid cloud strategy:
- Do not overprovision resources. Select instance types and storage options that match the actual needs of your workloads.
- Use auto-scaling to lower expenses during periods of lower activity.
- Minimize data transfer costs with regional placement of resources.
- Implement tagging for resources to categorize and track exact costs by projects, departments, or purposes.
- Regularly search for and remove unused or underutilized resources to avoid unnecessary costs.
- Use tools to gain insights into expenditure patterns. Analyze expenses over time and adjust usage accordingly.
Our article on cloud cost management tools presents 24 different platforms you can use to prevent higher-than-necessary cloud bills.
Start Your Hybrid Cloud Journey with Confidence
Creating an effective hybrid cloud strategy is not easy, so breaking the process down into manageable steps drastically increases your chances of success. Use what you learned in this article to get your strategy off to a good start and avoid the most common pitfalls companies fall into when devising a hybrid cloud.