As of version 5.1.23, MySQL does not feature a direct command to rename a database. The RENAME DATABASE command was removed due to its flawed design, which increased the chance of accidental data loss.
Removing the command made renaming MySQL databases more complicated, but multiple methods still exist to perform this action.
This guide will show you four methods for renaming a MySQL database.
Prerequisites
- Command-line access to the system.
- MySQL installed (learn how to install MySQL on Ubuntu and Windows).
- Access to a MySQL user with sufficient access privileges (e.g., root user).
- The cPanel server management software installed (optional).
- phpMyAdmin installed (optional).
Note: The RENAME DATABASE command is still available in the MySQL versions between 5.1.7 and 5.1.23. However, updating MySQL and using a renaming method listed in this guide is strongly recommended from a security perspective.
How to Rename MySQL Database
Depending on the type of MySQL installation and the configuration of the server, MySQL databases can be renamed using the following methods:
- The cPanel server management software.
- The server OS's command-line interface.
- MySQL CLI commands.
- The phpMyAdmin tool.
The sections below describe the procedure for each method.
Rename MySQL Database via cPanel
The cPanel interface offers the simplest way to rename a MySQL database. Follow the steps below to rename a database in cPanel:
1. Log in to cPanel.
2. Click MySQL Databases in the Databases section.
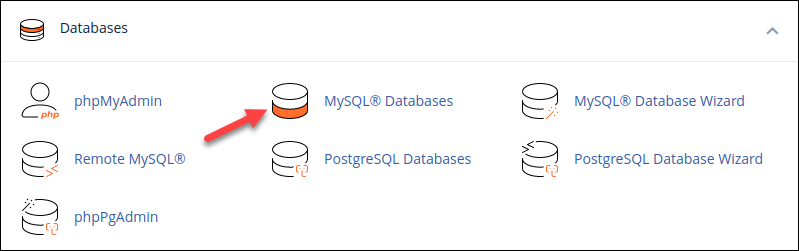
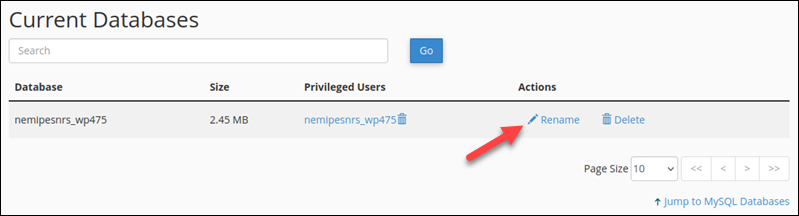
3. Select the Rename action in the Actions column for the relevant database.
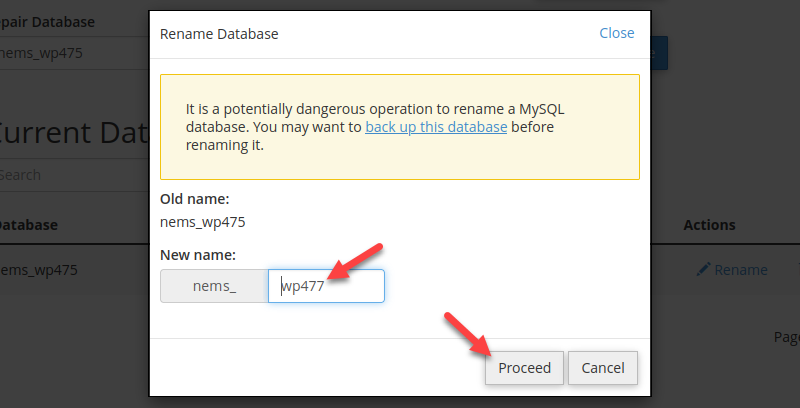
4. Type a new database name and click Proceed.
Renaming may take a long time if a database is large.
Rename MySQL Database by Dumping and Reimporting
On servers that do not support graphical interfaces, use the command line to:
- Export database content using mysqldump.
- Create a new database with mysqladmin.
- Move the old database content to the new database.
- Drop the old database.
Proceed with the following steps to rename a MySQL database using CLI:
1. Log into the server.
2. Create a dump file for the old database:
mysqldump -u [username] -p[password] -R [database] > [database].sqlReplace [username] and [password] with the actual credentials for the database, and replace [database] with the name of the database. There should be no space between -p and the password. The -R flag indicates that the dump file should retain all stored procedures and functions.
For example, to create a dump file for a database named testDB with the user admin and the password test1234, type:
mysqldump -u admin -ptest1234 -R testDB > testDB.sql3. Create a new blank database by using the mysqladmin command:
mysqladmin -u [username] -p[password] create [database]4. Import the dump file into the new database:
mysql -u [username] -p[password] [new-database] < [old-database].sql5. Optionally, remove the old MySQL database by dropping it:
mysqladmin -u [username] -p[password] drop [old-database]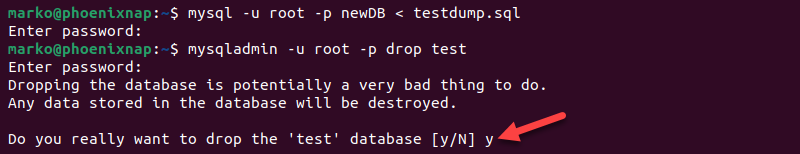
Rename MySQL Database via InnoDB (RENAME TABLE)
The InnoDB storage engine is included in all versions of MySQL since MySQL 5.5. Using InnoDB, admins can rename each table in a database to make it part of another database, effectively renaming the old database.
Proceed with the steps below to rename a MySQL database with InnoDB using the manual method or an automation script.
Manually Rename MySQL Database
Databases with fewer tables can be renamed using the manual method described below:
1. Create a new empty database:
mysqladmin -u [username] -p[password] create [new-database]Replace [username] and [password] with user credentials and [new-database] with a name for the new database.
2. Log into the MySQL shell:
mysql -u [username] -p[password]3. Use the RENAME TABLE command to change the table name:
RENAME TABLE [old-database].[table-name] TO [new-database].[table-name];Replace [table-name] with the name of a table in the existing [old-database] database. Repeat this action for each table in a database. For example, move the table_test table from testDB to newDB by typing:
RENAME TABLE testDB.table_test TO newDB.table_test;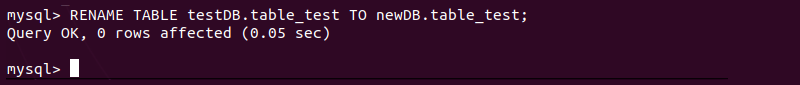
Rename Database Using Shell Script
For databases with many tables, execute the script below in the server OS shell to rename all the tables with a single command:
for table in `mysql -u root -p[password] -s -N -e "use [old-database];show tables;"`; do mysql -u root -p[password] -s -N -e "use [old-database];rename table [old-database].$table to [new-database].$table;"; done;Replace [username] and [password] with user credentials and [old-database] and [new-database] with the relevant database names. The script cycles through each table in the database and renames it.
Rename MySQL Database in phpMyAdmin
If you have access to phpMyAdmin, you can quickly rename a database by following the simple procedure described below:
1. Start phpMyAdmin. In cPanel, the tool is located in the Databases section.
2. Select a database from the menu on the left side of the screen.
3. Click the Operations tab in the tab menu at the top of the screen.
4. Provide the new database name in the Rename database to field.
5. Select the Go button.
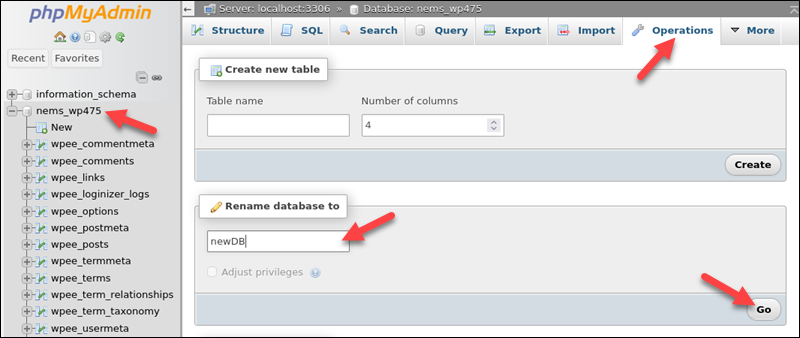
phpMyAdmin automatically renames the database.
Conclusion
After following this guide, you should know how to rename a MySQL database. The article covered four popular renaming methods: cPanel, the server's CLI, InnoDB, and phpMyAdmin.
Next, find out how to rename a column in MySQL.
