The docker exec command is a Docker CLI utility for interacting with running Docker containers. It allows execution of new commands directly within an active container's environment, which is particularly useful for debugging, inspection, and maintenance.
This article shows how to use the docker exec command and provides practical examples.

docker exec Command Syntax
The docker exec command requires the container's ID or name to identify the target environment for command execution:
docker exec [options] [container_id_or_name] [command]The container identifier is preceded by [options], i.e., additional parameters that modify the execution behavior, and followed by the [command] to be executed within the container, along with any arguments.
docker exec Options
A variety of options can be used to modify how docker exec behaves and control aspects such as interactivity, pseudo-terminal allocation, and environment variables.
Commonly used options include:
-d,--detach. Executes the command in detached mode, i.e., the process runs in the background.-i,--interactive. Keeps STDIN open, even if not attached, essential for interactive shell sessions.-t,--tty. Allocates a pseudo-TTY, often used in conjunction with-ifor interactive shell access.-e,--env. Sets environment variables for the command executed within the container.--user. Specifies the username or UID to use for the executed command.--env-file. Loads environment variables from a file.<b>-w</b>,--workdir. Sets the working directory inside the container.
docker exec vs. docker run
Both docker exec and docker run execute commands, but they operate on different scopes. docker run starts a new container from an image and runs its command as the container's primary process. In contrast, docker exec executes a command within an already running container, utilizing its existing environment and resources.
The table below sums up the main differences between the two commands:
| docker exec | docker run | |
|---|---|---|
| Container Status | Requires an existing, running container. | Creates and starts a new container. |
| Process Type | Executes a new process inside the container's environment. | Executes the primary process of a new container. |
| Purpose | Debugging, maintenance, or inspection of an active service. | Deployment, initial setup, or running a main application. |
docker exec vs. docker attach
docker exec initiates a new process inside a running container, independent of the container's initial command. This new process has its own lifespan and helps execute distinct, isolated tasks. Conversely, docker attach connects the local standard input, output, and error streams to the main process already running inside the container.
Connecting via docker attach ties the session to the container's primary process. If that process terminates, the attachment ends and, often, the container stops. Using docker exec allows users to run supplemental tools or shells without impacting the container's main service process.
docker exec Command Examples
The versatility of docker exec makes it applicable for a wide range of operations. The following sections demonstrate common use cases in container management and troubleshooting.
Interactive Shell Access
Opening an interactive shell session inside a container is the most frequent use case for debugging and environment inspection. The combination of the -i (interactive) and -t (TTY) options is essential for a functional shell session.
The example below shows docker exec starting a Bash shell session in a container named nginx:
docker exec -it nginx /bin/bash
Running Diagnostic Commands
Executing a non-interactive diagnostic command provides quick insight into the container's state without launching a persistent shell. This process is often used to check network configuration or resource usage.
The following example runs the env command to output all environment variables set in that container's context.
docker exec mysql env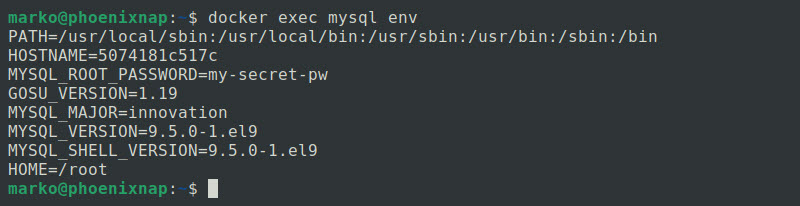
Executing as Different User
Specific tasks might require execution under a non-root user for security or permission-related reasons. The --user option allows the user ID or name to be specified.
The whoami command in the following example is executed in the php_app container by the user named www-data:
docker exec -it --user www-data php_app whoami
Creating File
Administrative tasks often involve creating, editing, or removing files for configuration or testing purposes. A simple command can be executed to verify permissions or deploy a temporary file.
The example below creates a file named test_file in the tmp directory of the mysql container:
docker exec mysql touch /tmp/test_fileRunning Command in Detached Mode
It is recommended that long-running maintenance or cleanup scripts be executed in the background to avoid blocking the current terminal session. The -d (detach) option enables non-interactive execution.
The following example uses the detached mode to start the cleanup.sh script in the container named log_analysis:
docker exec -d log_analysis sh /scripts/cleanup.shdocker exec Advanced Usage
Beyond basic shell access, docker exec supports more sophisticated use cases involving environment variables and complex command piping. For instance, executing a script and piping its output for immediate inspection is possible without saving intermediate files.
Setting environment variables using the -e option before the command execution matters when the operation depends on specific configuration parameters not present in the container's base environment. This action enables dynamic execution logic for scripts or utilities within the container.
The command below runs a Python script named script.py inside a running container named reporting_test, while temporarily setting the environment variable DEBUG_LEVEL to the value of five for that specific execution:
docker exec -e DEBUG_LEVEL=5 reporting_test python script.pydocker exec Errors and Troubleshooting
Understanding common errors is necessary for effective troubleshooting when using docker exec. Errors typically relate to container status, identifier issues, or command path problems.
Error: Container Not Running
The Container Not Running error occurs when the specified container stops unexpectedly. The docker exec command requires an operational container process space to execute a new command within it.
Resolution involves confirming the container's status with docker ps and restarting it if necessary.
Error: No Such Container
The Docker daemon reports the No Such Container error if the provided container identifier (name or ID) does not match any existing container. This error often occurs due to a typo or an attempt to connect to a container that has been removed.
Troubleshooting involves verifying the correct container name or ID using docker ps -a to list all existing containers.
Error: Exec Command Not Found
The Exec Command Not Found error indicates that the docker exec command successfully found the container and attached to it, but the specified command is not executable or accessible within the container's file system. This problem is common when using a short command name (like bash) on a minimal image that lacks the required utility.
The fix involves either specifying the full path to the executable (e.g., /bin/bash instead of bash) or verifying the executable exists in the container image.
Conclusion
The docker exec command's ability to launch new, independent processes within running containers facilitates essential tasks, from basic debugging to complex maintenance operations. Mastering its syntax and options is crucial for effective container management.
Next, read how to stop Docker containers.