McKinsey's annual research on the state of enterprise AI reveals that 72% of surveyed organizations have used AI in 2024. Just under 65% of respondents report regular use of generative AI (GenAI), nearly doubling from the previous year. Additionally, half of all surveyed companies state that they've adopted AI in two or more business functions, up from a third in 2023.
If you're considering joining the growing ranks of AI-powered companies, we're here to help you navigate the landscape and lay the groundwork for successful AI adoption.
This article offers an in-depth guide to enterprise AI that explains how companies use artificial intelligence to gain a competitive edge, reduce expenses, and unlock new business opportunities.
Check out our article on AI use cases if you'd like to learn about the most common applications of AI across major industries.
What Is Enterprise AI?
Enterprise AI is an umbrella term for the large-scale implementation of AI technologies within business environments, primarily aimed at automating processes and enhancing efficiency. By integrating AI across various business functions, organizations reduce operational bottlenecks, gain deeper insights from data, and become able to respond to market changes with greater agility.
In a few years, enterprise AI has evolved from simple rule-based automation to sophisticated machine learning (ML) models capable of independent adaptation.
Here's a list of the most commonly used AI technologies within corporate settings:
- Machine learning models capable of learning patterns from data to make predictions, detecting anomalies, and optimizing processes over time.
- Natural language processing (NLP) models that enable AI to understand, interpret, and generate human language in text or speech.
- Computer vision systems that allow AI to analyze, recognize, and extract information from images and videos.
- Deep learning models that power advanced neural networks and DNNs capable of identifying complex patterns in large data sets and making autonomous decisions.
- Robotic process automation (RPA) systems that automate repetitive physical tasks.
- AI-powered search models that improve relevance, better understand context, and retrieve more accurate information during searches.
- IoT and edge AI systems that process data locally on edge devices, enabling real-time insights and faster decision-making.
- Generative AI models that can create new content, such as text, images, or code, by learning from existing data.
Learn more about how knowledge generation works and how businesses use it to boost productivity and reduce business costs.
While a significant focus of enterprise AI is automating repetitive tasks, its primary goal is to augment human expertise. Rather than replacing employees, AI serves as a tool that enhances productivity, helps humans bypass mundane work, and speeds up innovation.

Enterprise AI Use Cases
Enterprise AI models enable companies to streamline repetitive tasks, reduce operational costs, and minimize the likelihood of human error.
Here's a list of the most common AI use cases within corporate settings:
- AI-powered customer support chatbots and virtual assistants that handle customer inquiries and improve service efficiency by speeding up response times.
- Fraud detection and risk management models that analyze transaction patterns to detect fraudulent activities. This type of fraud detection is one of the most popular use cases for ML in finance.
- AI algorithms that analyze historical sales data, market trends, and other relevant factors to make accurate sales predictions.
- Predictive analytics tools that forecast customer demand and help marketing teams create tailored retention and churn reduction strategies.
- AI-driven recommendation engines that tailor product and content suggestions based on user behavior.
- Compliance tools that use AI to monitor regulations, flag compliance violations, and automatically mitigate risks.
- AI-powered HR and talent management systems that assist in resume screening, employee performance analysis, and workforce planning.
- Intelligent document processing tools that automate file classification, data extraction, and contract analysis for legal, financial, and administrative tasks.
- AI-powered cybersecurity tools that detect anomalies in network traffic, identify potential threats, and perform predefined incident response actions.
- AI-based manufacturing tools that enhance quality control by analyzing sensor data and identifying patterns indicative of equipment failures.
- Supply chain optimization tools that use AI to forecast product demand, optimize inventory levels, and identify potential disruptions in the supply chain.
- AI-powered portfolio management tools used for risk assessment, automated trading, and financial modeling.
- Research and development of AI tools that analyze vast data sets and simulate outcomes to reduce the time and resources required for product development.
Check out our article on the use of AI in business for an in-depth overview of how companies use AI to streamline various tasks and processes.
Key Technology Considerations in Enterprise AI
Adopters of enterprise AI must carefully evaluate several key technological considerations to ensure the efficiency and security of their up-and-coming AI models. Here are the most critical factors:
- Hardware considerations. AI workloads require high-performance hardware, which commonly includes powerful GPUs, TPUs, and AI accelerators. You can set that hardware up on-site, in a public or private cloud, or rely on a hybrid cloud architecture.
- Data management and storage. Adopters require efficient ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) and ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) processes for handling both structured and unstructured data. Most companies use object storage solutions (S3, MinIO), distributed file systems (HDFS, Ceph), and databases optimized for AI workloads.
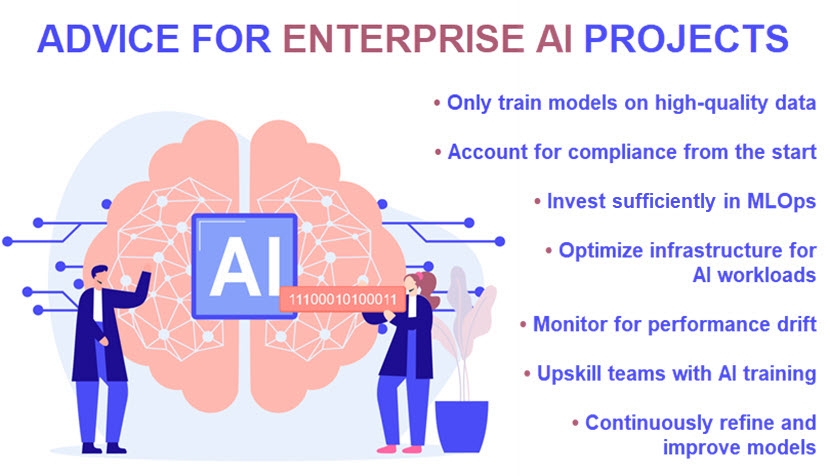
- Model development tools. The team developing your enterprise AI model needs access to deep learning frameworks and ML libraries like TensorFlow, PyTorch, Scikit-learn, and Hugging Face. These platforms drastically speed up model training.
- Security considerations. Adopters of enterprise AI must invest in sufficient security precautions that ensure the model and its inputs remain secure. Popular go-to measures include data encryption (at rest, in transit, and in use), tight access controls, adversarial attack protection, and differential privacy.
- AI governance. Enterprises must implement governance frameworks to ensure their AI models are fair, transparent, and accountable. Explainable AI (XAI) techniques are essential because they help interpret model decisions and mitigate bias in high-stakes business applications.
- Networking and connectivity requirements. Most enterprise-grade AI use cases require a low-latency, high-bandwidth infrastructure. Top-tier connectivity is also vital for large-scale AI training across distributed nodes.
- Cost considerations. Monitoring AI workload expenses and optimizing compute resource allocation is critical, especially if you rely on public cloud services. Using energy-efficient chips (e.g., ARM-based processors) to reduce power costs is also a smart investment for large-scale deployments.
Controlling your cloud spend is vital to the bottom line, so ensure your development team uses at least one cloud cost management tool.
Enterprise AI Advantages and Disadvantages
Let's explore the main advantages and disadvantages of enterprise AI that all potential adopters must know about before committing to any large-scale AI project.

Advantages
Enterprise AI offers several benefits that help organizations improve efficiency and decision-making processes. Here are the most notable advantages of enterprise AI:
- Automation of routine tasks. AI models automate repetitive and time-consuming tasks like data entry, scheduling, and customer support. Automating mundane tasks enables employees to focus on more strategic and creative work.
- Enhanced decision-making. Businesses can make data-driven decisions with greater accuracy with techniques like regression algorithms, classification models, clustering, and deep learning.
- Improved customer experience. The ability to speed up and personalize customer service is a common motivator for investing in enterprise AI. AI-driven chatbots and personalized recommendations improve customer interactions, while models can also help predict customer needs.
- Predictive analytics. Organizations can use AI to analyze historical data to forecast trends, behaviors, and potential risks. This strategy allows enterprises to anticipate market shifts, identify opportunities, and mitigate potential challenges before they cause issues. Predictive models can also analyze real-time data streams to make more adaptive and immediate forecasts.
- More reliable monitoring. AI's ability to process data in real-time enables organizations to implement near-instantaneous monitoring of business operations.
- Faster ROI. Automating various internal processes leads to shorter business cycles and speeds up the time it takes for companies to see results.
- Regulatory compliance. AI helps organizations adhere to industry regulations by automating risk assessments, monitoring transactions, and flagging potential compliance violations.
- Less chance of human error. Using AI on tasks that previously relied on manual work or traditional automation tools reduces the risk of costly mistakes. As an added benefit, AI and ML tools continuously improve process performance, so operations become more reliable over time.
- Cost reductions. By automating tasks, AI can drastically reduce costs in areas like customer service, logistics, and inventory management.
Disadvantages
Despite its numerous advantages, AI poses risks and dangers that you must be aware of. Here are the most notable downsides of enterprise AI:
- High initial costs. You'll need a hefty budget to acquire the necessary hardware and hire skilled professionals to develop and manage an AI model. The high price is a deterrent for many organizations.
- Implementation complexity. Integrating AI into existing business processes is complex and time-consuming, especially on an enterprise-grade scale. Adopters must often adjust their workflows, train employees, and restructure teams to work effectively alongside AI systems.
- Dependence on data quality. AI systems rely heavily on high-quality, accurate data. Poor-quality or incomplete data often result in inaccurate predictions or decisions. Models also often struggle with data drifts, which occur primarily when real-world data changes over time.
- Privacy and security concerns. Companies drastically increase the risk of violating data privacy regulations if the model's training or input data contains sensitive information. The use of AI also increases your attack surface for data breaches and leaks.
- Complex day-to-day maintenance. AI models require continuous monitoring to detect performance degradation and retraining on fresh data.
- Over-reliance on technology. Relying too heavily on AI makes organizations vulnerable to system failures or errors. If an AI system malfunctions, you may experience disruptions or operational risks as out-of-practice employees get back in control over automated tasks.
- Automation bias. This type of bias occurs when employees trust AI outputs too much and fail to verify their decisions.
- Lack of transparency. Complex AI models often suffer from unclear decision-making processes. This lack of transparency is highly problematic in critical areas like healthcare or finance, where accountability and explainability are essential.
- Bias and ethical issues. AI algorithms inherit biases present in their training data. In some cases, these biases can lead to discriminatory outcomes.
Enterprise AI and Private AI
The table below offers an overview of the main differences between enterprise and private AI:
| Point of Comparison | Enterprise AI | Private AI |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Designed to optimize and automate repetitive business processes on a large scale. | Focused on secure, in-house AI processing of proprietary or sensitive data. |
| Infrastructure | Typically runs on third-party cloud-based platforms. | Runs on private infrastructure, including on-prem servers, private clouds, or colocation centers. |
| Data Handling | Often involves external data processing and storage. | Keeps all data processing in-house, preventing exposure to third-party providers. |
| Security and Privacy | Data security largely depends on cloud providers' precautions and practices. | Offers full control over security policies and practices. |
| Compliance Considerations | Prone to risks due to using third-party infrastructure to process and store data. | Helps maintain compliance by keeping models within a controlled in-house environment. |
| Customization | Most third-party enterprise AI models can be fine-tuned via APIs or proprietary tools. | Fully customizable AI models built specifically for the organization's unique data and workflows. |
| Cost | Expensive due to reliance on cloud services, AI model licensing, and integration with enterprise systems. | High initial setup costs but lower long-term expenses due to a lack of cloud dependencies. |
| Latency and Performance | Enterprise AI (especially cloud-based) may suffer from network latency. | Offers low-latency, on-prem processing, which is crucial for real-time applications. |
| Scalability | Easily scalable on-demand thanks to cloud services. | Scaling requires hardware and infrastructure investments. |
| Model Training | Trained on a mix of third-party, open-source, and proprietary data. | Training occurs exclusively on proprietary and open-source data. |
| Maintenance and Updates | Hardware managed by external providers. Automatic updates and security patches. | Requires in-house hardware maintenance, updates, management, and ongoing model retraining. |
| Common Use Cases | On-prem AI for financial risk assessments, secure healthcare diagnostics, legal document analysis, and government AI applications. | On-prem AI for financial risk assessments, secure healthcare diagnostics, legal document analysis, and government AI applications. |
Check out our article on machine learning projects if you'd like to test your team's AI development know-how and see whether they would benefit from some upskilling.
How to Implement Enterprise AI?
Implementing enterprise AI from scratch requires a well-planned strategy that takes into account long-term business goals and available resources. Before diving into the technical aspects, the company should clearly define what it hopes to achieve with AI, such as:
- Automate repetitive back-office tasks (e.g., invoice processing, payroll management, data entry).
- Optimize sales operations using AI-driven demand forecasting.
- Streamline IT operations with predictive maintenance and automated troubleshooting.
Once you know what you aim to accomplish with AI, evaluate the existing IT infrastructure to understand whether you need upgrades to support your use case. This step includes auditing hardware and software, plus assessing data storage and processing power resources (in the cloud and on-prem). Network capacity (bandwidth, latency) is also a key consideration, especially for distributed AI workloads.
Next, gather and organize training data. AI relies on high-quality data for training and producing meaningful insights. The company should:
- Collect, clean, and label relevant data (e.g., customer info, operational data, financial records).
- Ensure data is stored securely and can be easily accessed for analysis.
- Address data privacy or compliance concerns (GDPR, HIPAA, etc.) from the start.
The next step is to choose the right AI stack. Select frameworks, platforms, and tools that fit the company's goals, infrastructure, and the team's skill set.
Once everything's in place, you can begin developing the AI model, which involves:
- Using the available data to teach the AI system how to recognize patterns, make predictions, or automate tasks.
- Continuously testing the model on real-world data to ensure it meets the business objectives and performs effectively.
- Fine-tuning the model's hyperparameters based on feedback and performance to improve accuracy.
Finally, carefully integrate the new model into relevant processes and applications, such as CRM systems, ERP software, or customer service platforms. Ensure you account for the new attack vectors during integration.
Read our article on the market's best AI processors if you've decided to run AI or ML workloads on on-site hardware.
How Can phoenixNAP Help with Your Enterprise AI?
If you do not have a private data center or a sizable on-site server room, phoenixNAP's colocation services enable you to set up your hardware at our Phoenix-based state-of-the-art facility.
Our colocation services provide the high-performance infrastructure, scalability, and cooling efficiency needed for enterprise-grade AI workloads, all without the overhead of maintaining a private facility. Setting up hardware at a colocation data center is an excellent choice for enterprise AI use cases if you:
- Require complete control over your AI hardware and infrastructure.
- Handle sensitive or regulated data that cannot be processed or stored in a public cloud.
- Have relatively predictable AI workloads (e.g., ongoing training, inference, or analytics).
- Need low-latency, high-bandwidth network performance with high uptime guarantees.
Here are the most notable selling points of deploying your AI-running hardware at our Phoenix-based facility:
- Over 100,000 sq. ft. of floor space (530,000 sq. ft. expansion underway).
- A historically disaster-free region.
- A global network backbone of 9+ Tbps.
- Two meet-me-rooms.
- A total of 45 carriers available.
- One of only 14 data centers in the U.S. offering access to all three major hyperscale cloud providers, including AWS Direct Connect and Google Cloud Interconnect.
- SOC 1, SOC 2, and SOC 3-compliant.
- HIPAA, GDPR, SOX, and GLBA-ready.
- 2N redundancy for critical infrastructure components.
- SLA-backed uptime for temperature, humidity, networks, and power.
As an extra benefit, sign a 3-year-long colocation contract to get 3 months of free hosting. Learn more about this offer on our colo promotions page.
Want a firsthand look at pNAP's flagship data center? Schedule a virtual tour of our Phoenix facility via our colocation page and see for yourself what makes us the go-to interconnectivity hub of the U.S. Southwest.
What Business Aspects Can You Improve with AI?
AI is profoundly changing the way companies get work done, so expect businesses to continue experimenting with how models can help them save money and boost efficiency. Use what you learned in this article to assess what segments of your organization would benefit the most from AI and start developing a strategy to implement AI where it can deliver the greatest impact.