A hyperscale data center is purpose-built to provide the most efficient environment for the world's most advanced compute and data storage needs. These vast facilities, often the size of multiple football fields, hold thousands of servers that work in tandem to process data at incredible speeds.
However, these facilities are more than just server farms. Hyperscale data centers are finely tuned ecosystems with advanced automation and scalability that allow seamless handling of fluctuating workloads and ensure high performance under any demand.
This article provides an in-depth guide to hyperscale data centers that covers everything you must know about these state-of-the-art facilities. Read on to learn how these colossal facilities operate and see what role this type of data center plays in the IT landscape.
What Is a Hyperscale Data Center?
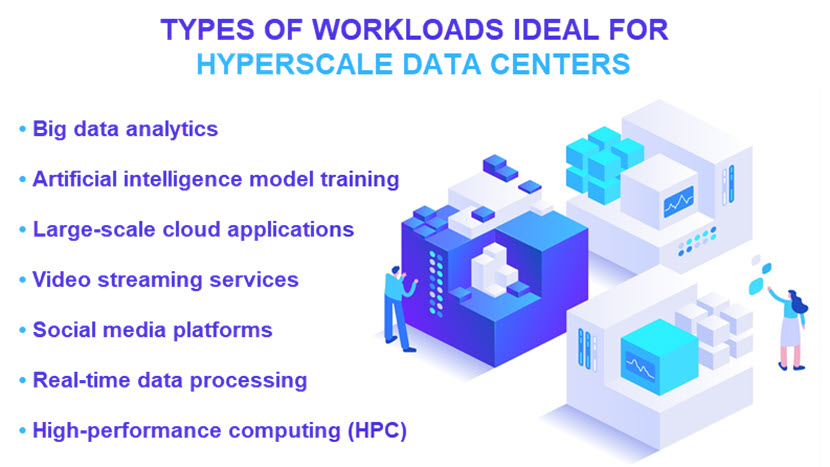
A hyperscale data center is a facility designed to support thousands of servers that work in parallel to handle large-scale workloads. These data centers support resource-intensive applications that require continuous data processing and real-time responses (public cloud computing, big data processing, large-scale artificial intelligence (AI) models, etc.).
Hyperscale data centers rely on a distributed computing model in which thousands of servers and storage devices work together as a cohesive system. This approach enables machines to process data in parallel, significantly increasing speed, efficiency, and the ability to handle large volumes of data.
Here are the main characteristics of a hyperscale data center:
- Massive scale and size. Hyperscale facilities often span hundreds of thousands of square feet and house tens of thousands of the same-size servers.
- High-density infrastructure. The rack density in hyperscale facilities is far higher than in standard data centers and server rooms. High-density infrastructure enables operators to maximize physical space (i.e., to fit in more computing power per square foot).
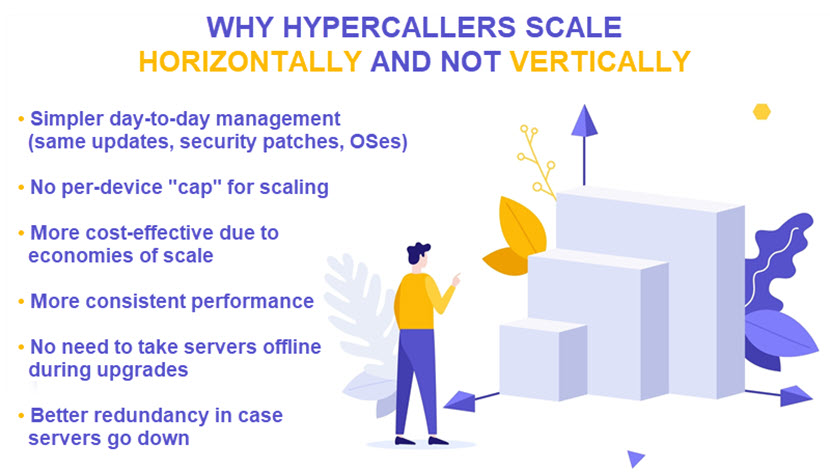
- Horizontal scaling. Hyperscale data centers rely primarily on horizontal scaling. The facility adds more same-sized servers to the cluster to meet the current needs, thereby sharing the workload across a larger pool of devices during periods of increased demand.
- Advanced networking. Hyperscale data centers employ high-speed, low-latency networking to enable seamless data flow between servers.
- Modular design. Organizations build a hyperscale data center in a way that enables them to expand the facility quickly with new server racks. This modularity eliminates the need for downtime during expansions or upgrades.
- Automation. Hyperscale data centers rely heavily on automation for tasks like server management, scaling, and performance monitoring.
- Energy efficiency. Hyperscale facilities incorporate cutting-edge energy management strategies to optimize power usage. Techniques like advanced cooling solutions, AI-driven power monitoring, and renewable energy sources are standard implementations.
With so much equipment, it's unsurprising that hyperscale facilities need massive amounts of power. Some hyperscale data centers consume enough electricity to power a small city, so efficient power designs are vital to the sustainability of these facilities.
Hyperscaler Services
Most hyperscale data centers are dedicated solely to serving the needs of the owner organization (i.e., the hyperscaler). However, some facilities also offer services to external companies that require hyperscale capabilities.
Hyperscalers deliver services on a scale that traditional data centers cannot match. These facilities offer resources that support large-scale, flexible, and rapidly evolving business needs. Here is an overview of what services companies most commonly rent from a hyperscale data center:
- Highly scalable virtual machines (VMs) and containerized environments.
- Data warehousing solutions for storing and organizing large data sets.
- Platforms for training and running AI and machine learning (ML) models.
- Tools for large-scale data ingestion, processing, and real-time analytics.
- Large-scale network services (e.g., VPNs or content delivery networks (CDNs)).
- Extensive data backup and disaster recovery options.
- Managed database services that support diverse database types.
While it is possible to rent these services from a non-hyperscale data center, companies use hyperscalers when they require highly scalable services capable of handling vast, dynamic workloads.
Unlike fixed-capacity data centers, hyperscalers offer total elasticity. Resources like computing power and storage can be scaled up instantly without a realistically reachable upper cap. This feature makes hyperscale data centers valuable for companies with millions of users who expect uninterrupted service.
Hyperscalers provide third-party clients with self-service portals for deploying resources and managing configurations, eliminating the need for support team reliance. This strategy drastically improves response times to client requests.
Unlike colocation facilities, a hyperscale data center never allows clients direct access to any physical equipment. Instead, users access all services online, and the only personnel allowed on-site is the hyperscaler's in-house team.
Hyperscale Data Center Benefits
While highly expensive and challenging to manage, hyperscale data centers offer advantages that other types of facilities cannot provide. Below is a close look at the most notable benefits of hyperscale data centers compared to more traditional hosting environments.
High Performance
One of the main selling points of hyperscale data centers is that they can handle vast amounts of data and demanding workloads efficiently. This benefit stems from several factors:
- Massive computing power. Hyperscale data centers deploy thousands of servers that process workloads in parallel. Such a setup provides the immense computing power necessary to support large-scale applications.
- Custom configurations. Hyperscalers use tailored server designs optimized for specific workloads (e.g., AI, ML, big data analytics). Highly specialized configurations guarantee top performance for suitable tasks.
- Low-latency connectivity. All hyperscale data centers implement high-speed networking technologies. Top-tier networking minimizes latency and ensures quick data transfers. Hyperscalers also use software-defined networking (SDN) to improve bandwidth utilization.
- Elastic scalability. Hyperscale facilities dynamically allocate resources based on real-time demand. Such a capability enables seamless handling of usage spikes without degradation of performance.
- Reliance on AI. Hyperscale data centers use AI to optimize resource distribution and predict maintenance needs. These practices keep performance levels consistent over time.
- High-performance storage systems. Hyperscale data centers utilize advanced storage technologies like NVMe and SSDs to deliver fast read and write speeds for data-intensive applications. These facilities also implement distributed file systems that enhance data accessibility and retrieval speed.
- Robust cooling systems. Efficient cooling systems help hyperscalers maintain optimal operating conditions for hardware. The lack of temperature fluctuations prevents thermal throttling and helps ensure consistent performance.
Our article on data center cooling takes you through everything you must know about keeping facilities at optimal temperatures.
Unparalleled Scalability
Top-tier scalability is one of the defining features of a hyperscale data center. These facilities are flexible enough to adapt in real-time to workload changes. This feature is crucial for businesses looking to meet complex, fluctuating demands without worrying about capacity constraints.
A key feature of hyperscale facilities is their horizontal scaling approach that allows for rapid resource allocation across a distributed architecture. Horizontal scaling refers to the practice of adding more machines or nodes to a system rather than increasing the capacity of existing machines (i.e., what companies do during vertical scaling).
Instead of relying on dozens of powerful servers, hyperscalers utilize thousands of standard, same-size servers. Servers run in pods, each containing multiple servers that work together to process assigned workloads. When there is a need for more processing power, the facility automatically spreads the workload over a larger number of pods.
Hyperscale data centers use automated load balancers to distribute incoming traffic and workloads across servers. Load balancers continuously monitor server performance and user demand, dynamically reallocating resources as needed. If one server experiences high traffic, the load balancer redirects requests to underutilized servers.
Unlike traditional data centers, hyperscale facilities' design allows for continuous expansion by adding new server pods without overhauling the entire facility. Resources can theoretically grow indefinitely, making it feasible for companies to support massive applications, large data lakes, or high-performance computing needs without a realistic upper cap.
High Levels of Automation
Hyperscalers use automation to enhance efficiency, reduce the chance of human error, and enable real-time scaling. Automation allows hyperscale data centers to function with minimal human intervention.
Here's an overview of what tasks and processes hyperscalers commonly automate at their facilities:
- Deployment and configuration of new server pods and storage systems.
- Continuous tracking of system performance metrics, memory consumption, and network traffic.
- Responses to anomalies and potential breaches detected by security systems.
- Dynamic workload distributions across server pods.
- Computing power and storage capacity scaling in response to real-time usage levels.
- Backup processes and recovery procedures.
- Application of software updates and security patches to servers and applications.
- The monitoring of temperature, humidity, and other environmental factors.
- Orchestration of network setups and configurations.
Hyperscalers use AI and ML technologies to orchestrate and automate processes. These systems continuously analyze performance data, predict traffic patterns, and adjust resource allocations in real-time to ensure optimal efficiency.
AI is driving significant transformation in the data center industry. Our article on the impact of AI on data centers explains how facility owners have adapted to the recent technological advances.
Fault Tolerance and Redundancy
High fault tolerance and redundancy levels at hyperscale data centers ensure that operations remain uninterrupted and resilient during unforeseen disruptions. This reliability is essential for maintaining high availability for businesses that require continuous access to data and applications.
Here's an overview of why a hyperscale data center is so resilient to incidents:
- Multiple power sources. Hyperscale data centers have multiple power feeds and backup generators to ensure a continuous power supply. This precaution minimizes the risk of downtime due to power failures or local outages.
- Network redundancy. All hyperscalers implement redundant connections with diverse routes to prevent single points of failure in case of network-related problems.
- Real-time data mirroring. Hyperscale data centers use various data replication strategies to maintain copies of critical data across multiple server racks or even locations.
- Automated failover mechanisms. Automated failover systems detect failures and switch operations to backup servers without manual intervention. That way, hyperscalers reliably meet even the most demanding RTO requirements.
- Health monitoring. Hyperscalers continuously monitor system health. Round-the-clock monitoring allows for rapid identification of potential issues and enables preemptive action before failures impact operations.
- Resilient architecture. Distributing workloads across multiple servers enables hyperscalers to ensure that if one server fails, others can take over without affecting overall performance.
- Global resilience. Many hyperscalers operate multiple data centers across geographically diverse locations. Global distribution allows them to quickly reroute workloads to other locations in case of regional issues.
These features make hyperscale data centers an attractive option for enterprises with high uptime requirements. By ensuring minimal downtime and providing rapid recovery capabilities, hyperscale data centers offer the level of reliability that enterprises need to maintain business continuity at all times.
Cost Efficiency Through Economies of Scale
Hyperscale data centers benefit significantly from bulk purchasing power. Facilities can negotiate lower prices on servers, storage devices, and networking equipment by buying them in large quantities. Additionally, long-term relationships with hardware suppliers often lead to better terms, which further drives down costs.
Most hyperscalers invest heavily in energy-efficient technologies. Advanced cooling systems, such as free air cooling and liquid cooling, help reduce energy consumption compared to traditional data centers. Many hyperscale operators also invest in renewable energy sources, which further lowers operating costs in the long run.
Automated resource allocation also contributes to overall cost efficiency. The ability to scale down resources in real-time during lower usage ensures the facility never wastes capacity. Meanwhile, efficient load balancing optimizes the use of available resources, maximizing throughput while minimizing operational costs.
Standardized equipment also leads to cost reductions. Using standardized hardware and software reduces complexity, making it easier to manage and maintain systems. A consistent technology stack also helps operators reduce the costs associated with staff onboarding and ongoing education.
Want a tighter grip over your IT budget? Our article on IT cost reductions presents 12 tried-and-tested strategies for lowering expenses without causing long-term consequences.
Hyperscale Data Center Challenges
Hyperscale data centers offer unique benefits, but they also face several notable challenges due to their massive size and operational complexity. Here are some of the most notable challenges companies face when running a hyperscale data center:
- High energy consumption. Hyperscale data centers require enormous amounts of power to operate. Managing this consumption sustainably and cost-effectively is a constant challenge.
- Cooling and heat management. Cooling a hyperscale data center is challenging due to high pod density. Traditional cooling methods are often inefficient, so hyperscalers must experiment with advanced cooling techniques.
- Complex infrastructure management. Ensuring high availability, security, and efficient resource allocation at this scale is challenging. Hyperscalers depend heavily on advanced automation, but even minor issues can have significant ripple effects across systems.
- Hardware maintenance. Hyperscale data centers have significant maintenance demands. Hardware failures are inevitable, so the facility requires continuous monitoring and prompt replacements to avoid disruptions.
- Location and proximity issues. Hyperscalers build facilities in areas far from major populations, which often causes issues for latency-sensitive applications. Relying solely on distant hyperscale facilities can lead to a suboptimal user experience if the hyperscaler does not utilize edge servers.
- Compliance concerns. Hyperscalers handle massive amounts of data from various industries and regions, which complicates data security and regulatory compliance. Meeting diverse and evolving regulations requires meticulous data handling practices.
- Environmental impact. The environmental impact of hyperscale data centers is a growing concern. Large energy consumption and carbon emissions are significant challenges, so achieving sustainable operations remains a complex issue for hyperscalers.
Our article on data center sustainability presents the most effective ways organizations can minimize the environmental impact of their hosting facilities.

Hyperscale Data Center Examples
Here are a few notable examples of hyperscale data centers that stand out in terms of sheer size and advanced infrastructure:
- Inner Mongolian Information Hub. This massive data center in Hohhot, China, supports operations for companies like Alibaba and Tencent. This facility spans a total area of 10.7 million square feet.
- The Citadel Campus. This facility in Tahoe Reno, Nevada, belongs to Switch. It's powered by 100% renewable energy and consumes up to 650 megawatts (MW) of power at peak demand. The Citadel Campus guarantees a latency of 4.5 milliseconds (ms) to Silicon Valley.
- Google data centers. Google has hyperscale data centers in Iowa (USA), Hamina (Finland), and Singapore. These centers support Google Search, YouTube, and Google Cloud. A stand-out feature of these facilities is that they rely on seawater cooling and advanced regression algorithms for energy optimization.
- Microsoft data centers. Microsoft's hyperscale data centers power services like Office 365 and Xbox Live. This corporation has hyperscale facilities in Quincy, Washington, and Dublin, Ireland.
- Meta (Facebook) data centers. Meta's hyperscale data centers, located in places like Prineville, Oregon, and Luleå, Sweden, power platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp. The Sweden-based facility relies on outdoor air cooling that leverages the cool Scandinavian climate.
- Alibaba data centers. Alibaba's hyperscale data centers support its massive e-commerce operations. With major facilities in Zhangbei (China) and Dubai, Alibaba prioritizes AI-driven energy management and water-based cooling methods to handle massive traffic.
- Apple data centers. Apple has hyperscale data centers in locations like Maiden, North Carolina, and Reno, Nevada. These massive facilities power services like iCloud, iTunes, and the App Store.
The choice of where to build a data center has major implications on how well the facility will operate. Our data center site selection article outlines everything companies consider when deciding where to construct a new facility.
How to Choose a Hyperscale Data Center Provider
Below are some practical tips that will help you choose a hyperscale data center provider that aligns with your organization's goals, performance requirements, and budget constraints:
- Look for providers with data centers in regions close to your user base to ensure minimal latency for your hosted services.
- Inquire about the speed at which you can scale resources up or down, particularly during peak business periods or unexpected demand surges. Some providers impose "soft" limits, so find out whether these constraints impact your ability to scale.
- Ensure the hyperscaler has sufficient data center security measures and precautions. Verify encryption standards and inquire about role-based access controls to ensure your assets will be fully secure.
- Choose providers with multi-region or multi-zone redundancy to ensure your services will stay online during unforeseen localized disruptions.
- Ensure the provider complies with industry-specific regulations and holds relevant certifications (GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2, etc.).
- See if the provider offers tools that enable you to implement efficient backup and disaster recovery (BDR) measures.
- Search for providers who offer dedicated direct connections for faster and more secure access to your infrastructure.
- Review SLAs for uptime guarantees, response times, and compensation policies in the event of outages. Choose a provider that offers strong assurances.
Hyperscale providers often have complex pricing models. Make sure you understand how services are billed to avoid unexpected costs. An excellent way to save money is to look for providers that offer discounts for reserved instances and long-term commitments.
Many hyperscale providers offer trial periods for new customers. Use these trials to test performance, assess ease of use, and ensure compatibility with your applications. This opportunity enables you to see how well a hyperscaler's platform aligns with your IT needs in realistic settings.
The Backbone of Large-Scale Modern IT
While only a handful of organizations have a genuine need for hyperscale data centers, many large-scale use cases (cloud services, social media, complex AI models, etc.) are only feasible if they rely on hyperscale computing. These data centers offer immense capacity and scalability that traditional data centers cannot match, so expect hyperscale facilities to be at the center stage of cutting-edge IT in the coming years.



