Cybersecurity is a costly venture. Building and maintaining an in-house security team requires a substantial investment in skilled personnel and advanced technology. To address these challenges, many organizations are turning to Managed Detection and Response (MDR) services.
This article explores how MDR offers robust real-time protection without the hefty price tag of a fully staffed internal security team.
What Is Managed Detection and Response?
Managed detection and response is a cybersecurity managed service that protects organizations from advanced cyber threats with advanced technology, threat intelligence, and human expertise. MDR services provide continuous monitoring, threat detection, incident response, and remediation.
These services are typically delivered by third-party vendors, enabling organizations to outsource their cybersecurity operations while benefiting from specialized skills and innovative technologies.
How Does MDR Work?
Here is a detailed look at the core components and processes of MDR.
Threat Detection
Threat detection is the first and foremost function of MDR services. It involves identifying potential threats across an organization’s IT environment with the following tools:
- Endpoint detection and response (EDR). EDR systems continuously monitor endpoint devices (e.g., desktops, laptops, servers) to detect malicious activities such as unauthorized access, data breaches, and malware infections. They also provide detailed telemetry data that enables deep forensic investigations of cyber attacks.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM). SIEM systems aggregate and analyze log data from various sources, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, intrusion prevention systems, servers, and applications. SIEM systems use correlation rules and advanced analytics to identify potential security incidents based on patterns and anomalies.
- Intrusion detection systems (IDS) and intrusion prevention systems (IPS). IDS and IPS monitor network traffic for known attack signatures and behavioral anomalies. IDS alerts security teams to potential threats, while IPS can block malicious activities in real time.
- User and entity behavior analytics (UEBA). UEBA systems leverage machine learning and behavioral analytics to establish baselines of normal user and entity behavior. Deviations from these baselines indicate insider threats, compromised accounts, or other malicious activities.
Continuous Monitoring
MDR providers offer round-the-clock monitoring through various systems and processes to ensure real-time threat detection and response.
- 24/7 security operations center (SOC). MDR providers maintain SOCs staffed with experienced security analysts who continuously monitor client environments. These analysts use advanced tools and threat intelligence to detect and investigate anomalies.
- Behavioral analytics. Behavioral analytics uses algorithms to examine network traffic, user behavior, and system activities for unusual patterns that signify advanced persistent threats (APTs) and other complex attacks.
- Threat intelligence integration. MDR providers integrate global threat intelligence feeds into their monitoring systems to stay updated on the latest attacker tactics, techniques, and procedures. This integration enhances their ability to detect emerging threats and zero-day exploits.
Incident Investigation
When a potential threat is detected, MDR teams undertake detailed investigations to confirm its nature and assess its impact.
- Log analysis. Security analysts review logs from various sources to trace activities associated with the potential threat. This process includes examining event logs, network traffic logs, application logs, and system logs to identify indicators of compromise.
- Network traffic analysis. This process involves inspecting network flows and packet captures to identify malicious activities. Analysts look for unusual traffic patterns, such as data exfiltration, lateral movement, and communication with known malicious IP addresses.
- Forensic analysis. This process is conducted on affected systems to understand the attack vector, scope of compromise, and the attacker's methods. Forensic analysis may involve examining file systems, memory dumps, registry keys, and other artifacts to reconstruct the attack timeline and identify the root cause.
Response and Remediation
After confirming a threat, MDR providers mitigate its impact and prevent further damage. This process involves:
- Containment. Containment measures involve isolating affected systems to prevent the spread of malware or further data exfiltration. This process includes quarantining infected endpoints, blocking malicious IP addresses, and disabling compromised accounts.
- Eradication. This stage involves removing malicious files, closing vulnerabilities exploited by attackers, and cleaning up compromised systems. After the initial eradication, MDR providers deploy patches, update security configurations, and run antivirus/anti-malware scans.
- Recovery. This step focuses on restoring affected systems and data to their pre-incident state and ensuring business continuity. This process may involve restoring from backups, reimaging compromised systems, and validating the integrity of critical data.
- Post-incident reporting. After an incident, MDR providers generate detailed reports that include root cause analysis, remediation steps taken, and recommendations for preventing future incidents. These reports provide valuable insights for improving security and addressing gaps.
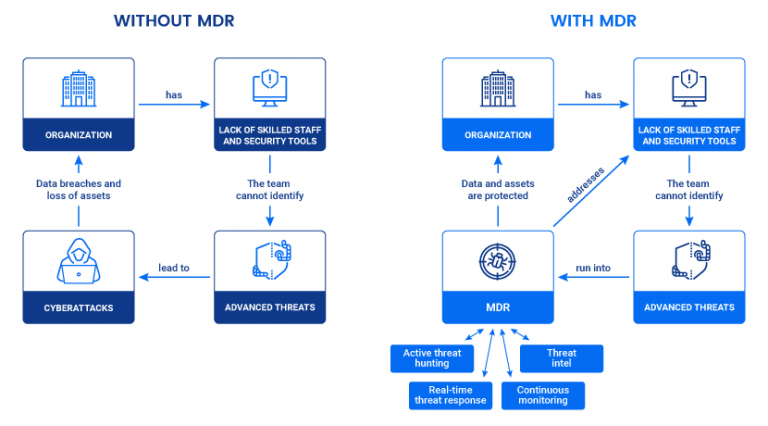
What Challenges Does Managed Detection and Response Solve?
MDR services address several critical challenges.
Limited In-House Expertise
Many organizations lack specialized cybersecurity expertise to detect and respond to advanced threats effectively. Additionally, retaining experienced cybersecurity professionals is challenging due to high demand. MDR providers offer access to teams of experienced security analysts, threat hunters, and incident responders with deep knowledge of the latest attack techniques.
Resource Constraints
Building and maintaining a comprehensive security infrastructure, including a fully functional SOC, is resource-intensive. MDR services provide scalable solutions that leverage shared resources, reducing organizations' financial and operational burden while delivering high-quality security services.
Rapid Threat Evolution
Cyber threats evolve rapidly, with new attack vectors, techniques, and malware variants constantly emerging. MDR providers continuously update their detection capabilities and threat intelligence to stay ahead of these changes and protect their clients against the latest threats.
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
Many industries are subject to stringent cybersecurity regulations and standards, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. MDR services help organizations achieve and maintain compliance by offering continuous monitoring, detailed reporting, and incident response capabilities that meet regulatory requirements.
Who Needs Managed Detection and Response?
Here are the primary groups that need MDR:
- Small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs). SMBs often lack the resources to build a full-fledged security team, making outsourcing their security needs practical and cost-effective.
- Organizations that manage sensitive data. This category includes healthcare, finance, and government entities, where data breaches have severe consequences. These organizations must prioritize data security to protect sensitive information and maintain trust.
- Organizations with strict compliance requirements. Industries governed by stringent regulations benefit from MDR services to meet compliance needs and ensure proactive incident response.
- Companies experiencing frequent cyberattacks. High-risk industries like technology, critical infrastructure, and energy are frequent targets of sophisticated attacks and thus require robust protection of their operations and assets.

The Benefits of Managed Detection and Response
Here are the key advantages of MDR.
Cost-Effectiveness
MDR services offer a cost-effective alternative to establishing an in-house security operations center. Here’s how they help:
- Reduced capital expenditure. By leveraging the provider's resources and expertise, MDR avoids hefty investments in security infrastructure and staff.
- Scalability. MDR providers can easily adjust services to match your organization's changing security needs.
- Predictable costs. MDR benefits from subscription-based pricing, making planning and managing your security budget easier.
Enhanced Reporting and Visibility
MDR services provide detailed insights into your security posture and incident handling. Benefits include:
- Regular reporting. MDR providers give comprehensive reports on security activities, incident responses, and overall security health.
- Custom dashboards. Most MDR providers offer real-time data and analytics through custom dashboards.
- Compliance documentation. Regular reporting and custom dashboards enable you to generate documentation required for compliance audits and regulatory reviews easily.
Faster Deployment
MDR services can be deployed quickly compared to setting up an in-house security operation.
- Rapid implementation. You can quickly set up and deploy MDR services, reducing the time to achieve complete operational security.
- Minimal setup. Implementing MDR avoids the lengthy processes involved in building and staffing an in-house SOC.
Types of Managed Detection and Response Providers
There are four types of MDR providers, each offering various levels of specialization and service. Understanding these types will help you choose the right provider.
- Pure-play MDR providers. Specialized firms focused exclusively on providing MDR services. These providers typically offer the most advanced and dedicated MDR capabilities.
- Managed security service providers (MSSPs) with MDR capabilities. Offer a broader range of managed security services, including MDR, often as part of a comprehensive security portfolio.
- Cybersecurity consultancies offering MDR. Provide MDR as part of a suite of cybersecurity consulting services, offering expertise in various aspects of cybersecurity.
- Cloud providers with MDR solutions. Include MDR capabilities as part of their cloud security offerings to protect cloud environments and workloads.
phoenixNAP has engineered the world's most secure cloud platform, Data Security Cloud, by integrating multiple layers of security, including advanced MDR capabilities.
Developed in partnership with industry leaders VMware and Intel, this cloud infrastructure platform delivers unparalleled data protection, vulnerability management, and endpoint security.

How to Choose a Managed Detection Response Provider?
Consider the following factors when evaluating potential providers.
Expertise and Experience
First, evaluate the provider's expertise and experience in detecting and responding to advanced threats. Ensure the provider's team holds relevant certifications, such as CISSP, CEH, or GCIA. Providers with industry-specific experience will better understand your sector's unique threats, regulatory requirements, and security challenges. Additionally, ask for case studies or references from other clients to assess the provider's performance and reliability.
Technology and Tools
Next, examine the provider's technologies and tools to ensure they meet your needs. Review the provider's use of detection tools like EDR, SIEM, IDS/IPS, and UEBA, and ensure they use a multi-layered approach to threat detection. To minimize disruption, the provider's tools must integrate seamlessly with your existing IT infrastructure and security systems. Look for providers that leverage advanced analytics, such as machine learning and artificial intelligence, for threat detection and analysis.
Service Level Agreements
Service level agreements (SLAs) define and mandate the level of service you can expect from a provider. Ensure the SLA specifies rapid response times for different incidents, including critical ones that require immediate attention. Confirm that the provider offers 24/7 support and availability for critical issues. Ensure the SLA establishes clear performance metrics on detection accuracy, false positive rates, and resolution times.
Compliance Support
Confirm that the provider knows your industry's regulatory landscape and can support your compliance efforts. The provider must also be able to offer detailed reports for audits and compliance checks. Look for comprehensive documentation practices that support compliance efforts, including incident reports, risk assessments, and policy reviews.
Customization and Scalability
Finally, assess whether the provider can tailor their services to your needs and grow with your organization. Ensure they can customize their strategies to fit your environment and offer scalable solutions that grow with your organization, accommodating changes in size, complexity, and security requirements.

The Challenges of Managed Detection Response
Implementing MDR presents several challenges. Understanding them will help you prepare effectively.
Integration with Existing Systems
Integrating MDR services with your existing IT infrastructure is often tricky.
- Compatibility issues. To avoid disruptions and ensure seamless integration, you must ensure that the MDR tools are compatible with your current systems, including legacy applications and custom software.
- Data integration. You must seamlessly integrate data sources from various security tools to provide a holistic view of the security landscape.
- Implementation time. Although implementing MDR is faster than building an in-house team, consider the time needed to fully integrate MDR services and achieve optimal performance, including initial setup, configuration, and tuning.
Dependence on Third-Party Providers
Relying on external providers for critical security functions introduces risks.
- Service disruptions. There may be a disruption in the service if the provider faces operational issues, such as outages, staffing challenges, or cyber incidents.
- Provider reliability. You must ensure the provider has robust continuity plans and can maintain service levels, even in adversity.
- Data privacy. You must thoroughly evaluate the provider’s data handling and privacy practices, as you will be entrusting them with your sensitive data.
Cost Considerations
While MDR is generally cost-effective, it still requires a financial investment.
- Subscription costs. The subscription fees for MDR services vary based on the size of the organization and the level of service required. Building an in-house security team is often more cost-effective for large organizations with extensive resources and a high volume of sensitive data requiring constant, tailored security measures.
- Additional expenses. There may be potential additional costs for extra services, customizations, or incident response, such as forensic investigations, threat hunting, and compliance reporting.
- Budget justification. You must justify the cost of MDR services based on their value in enhancing security and reducing risk, ensuring a clear return on investment.
Leveraging Expertise for Enhanced Protection and Efficiency
Outsourcing cybersecurity enables organizations to access expert knowledge and reduce costs by avoiding major investments in tools and staff. Managed detection and response (MDR) exemplifies how outsourcing can enhance security, though choosing the right provider is crucial to meet business needs and ensure data privacy and compliance.



