Data center networking is the backbone of modern IT infrastructure. It enables servers, storage systems, and applications to communicate efficiently. Data center networking also involves high-speed connections, switching fabrics, routing protocols, and security layers that ensure reliable data flow within and between facilities.
In a landscape of increasingly distributed and cloud-driven workloads, data center networking assumes the critical role in delivering low latency, scalability, and resilience. This way, data center networking improves operations for enterprise applications and AI workloads.
This article explains the importance of data center networking, how it works, and the challenges organizations face when implementing networking infrastructure within their data centers.

What Is Data Center Networking?
Data center networking refers to the design, deployment, and management of the communication infrastructure that connects servers, storage devices, and other computing resources inside your data center. This infrastructure encompasses both the physical hardware, including switches, routers, and cables, as well as the logical components, such as network protocols, virtualization technologies, and security mechanisms.
The purpose of data center networking is to provide high-bandwidth, low-latency, and highly available connectivity that allows applications and workloads to operate seamlessly across distributed environments. This networking layer must also support rapid scalability, enabling organizations to expand resources in response to demand while maintaining consistent performance.
In modern data centers, networking strategies often integrate automation, software-defined networking, and advanced traffic management to optimize resource use and ensure secure, resilient, and efficient data delivery across hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
Learn about other methods of data center resource optimization in our article on data center energy efficiency.
The Importance of Data Center Networking
Data center networking ensures reliable communication between servers, storage systems, and applications. It enables efficient operations and seamless data transfer to support cloud computing, AI, and other resource-intensive applications.
Here are the key factors that contribute to the importance of data center networking:
- A robust infrastructure foundation. As a backbone of modern IT, data center networking ensures seamless data transmission and processing. High availability and redundancy built into the network help prevent downtime, keeping the services accessible to users and business operations running.
- Ensuring optimal performance. Data center networking minimizes latency and enhances data flow, resulting in improved application performance and better end-user experience. Low latency, combined with high bandwidth, enables the smarter handling of massive data flows, AI workloads, and big data analytics.
- Scalability support. As businesses grow and workloads expand, the data center network must accommodate additional servers, storage, and applications without creating bottlenecks. A well-architected network enables seamless scaling, whether adding capacity on-premises or extending into hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
- Advanced security. Data center networking infrastructure serves as a defense against cyber threats by ensuring segmentation, monitoring, and controlled access to sensitive information and systems. Zero-trust architecture combined with microsegmentation protects increasingly distributed environments.
- Facilitating cost-effectiveness and operational efficiency. Modern approaches to data center networking, such as software-defined networking and automation, reduce manual management, optimize resource utilization, and cut operational costs. This way, organizations stay flexible and agile, with infrastructures that support both current business needs and future innovation.
Understanding why data center networking is essential is the foundation for exploring how it functions in practice, from the underlying architecture to the technologies that enable seamless communication.
How Does Data Center Networking Work?
Data center networking encompasses several steps that transform raw hardware and cables into a highly scalable and secure network infrastructure.
These steps include:
- Defining traffic patterns and reliability factors. Map east-west vs. north-south flows, latency/throughput targets, failure domains, and compliance constraints.
- Building the physical underlay. Deploy a non-blocking leaf-spine topology with high-speed links, consistent MTU configuration, and redundant paths. Standardize optics, cabling, and port layouts to simplify operations.
- Hardening edge attachment for hosts. Connect servers to a pair of leaves using LACP/MLAG (vPC) for link/node redundancy. Validate NIC offloads, MTU, and fast link failure detection for quick convergence.
- Creating tenant and L3 segmentation. Define VLANs and VRFs to isolate environments (production/development/tenant). Plan subnets and gateways per segment to contain broadcast domains and emphasize policy boundaries.
- Integrating storage networking. Choose FC/FCoE or IP-based storage (iSCSI, NVMe-TCP, or RoCEv2). For RoCEv2, ensure a properly configured lossless fabric using DCB features such as PFC and ECN to prevent congestion collapse. If using lossless transports (RoCEv2), configure DCB features like PFC and ECN carefully to avoid congestion.
- Applying quality of service and congestion management. Classify traffic (user, storage, control, telemetry), set queueing/priority, and enable ECN/WRED where appropriate. Align end-host and fabric policies to prevent head-of-line blocking.
- Automating configuration and lifecycle. Manage the fabric with intent-based/SDN controllers or IaC (Ansible/Terraform) via APIs. Use CI/CD pipelines, pre-change validation, and canary rollouts to reduce risk.
- Operating, testing, and optimizing. Run failure drills, capacity planning, and upgrade simulations. Track SLOs for latency, loss, and jitter, while iterating on design hot spots and buffer tuning as workloads evolve.
Each stage of data center networking builds upon the previous one, starting with the physical infrastructure and progressing through logical segmentation, overlays, security, and automation.
Data Center Network Components
Each component of data center networking has a specific role in a data center’s operations. From carrying data to enforcing security measures, here is a breakdown of the core components of data center networks.
Switches and Routers
These elements are the backbone of the data center network. Switches connect servers and storage devices in the data center. They then forward traffic across the fabric at high speeds, minimizing latency and ensuring scalability.
Routers, on the other hand, focus on handling traffic between networks, both inside the data center and to external sites and cloud providers. Routing protocols, such as BGP and OSPF, are used to determine the most efficient path for data packets.
Firewalls
Firewalls enforce security policies by inspecting packets at both the network (Layer 3/4) and application (Layer 7) layers. In a data center, they serve dual purposes: perimeter firewalls protect external-facing services, while internal segmentation firewalls limit lateral movement between workloads.
Modern firewalls often function as next-generation firewalls (NGFWs). They provide deep packet inspection, intrusion prevention, SSL/TLS decryption, and application-aware filtering. Many data centers now rely on microsegmentation and zero-trust models, where firewalls enforce policies close to workloads using distributed software firewalls or hypervisor-based agents.
Load Balancers
Load balancers optimize traffic distribution across servers, ensuring efficient use of resources and maintaining high availability. Layer 4 load balancers manage TCP/UDP flows, while Layer 7 load balancers can inspect HTTP headers, cookies, and content to make intelligent routing decisions.
Advanced implementations support SSL offloading, health checks, application acceleration, and global server load balancing (GSLB) across multiple data centers. Some load balancers are hardware appliances with dedicated ASICs for performance, while others are software-based or container-native, integrated directly into cloud or microservices architectures.
Cabling and Transceivers
The physical infrastructure includes structured cabling systems, usually made from copper or fiber, and optical transceivers. High-density fiber optics (OM4 multimode or OS2 single-mode) is common in large-scale data centers to support 40G, 100G, 200G, and now 400G+ Ethernet.
Transceivers such as QSFP28, QSFP-DD, or OSFP modules provide pluggable optics tailored to different distances and speeds. Proper cable management, polarity maintenance, and adherence to standards such as TIA/EIA-568 are crucial in supporting scalability and minimizing operational errors.
Network Interface Cards (NICs)
NICs in servers connect workloads to the network fabric. Advanced NICs, such as SmartNICs or DPUs (data processing units), offload functions like VXLAN encapsulation, encryption, QoS, and storage protocols (NVMe-oF, iSCSI, RoCEv2) from the CPU. These functions enhance performance and reduce latency for high-demand workloads, such as AI/ML, virtualization, and big data.
Multi-port NICs provide redundancy and link aggregation (LACP), while modern NICs support RDMA (Remote Direct Memory Access) to enable ultra-low-latency communication between compute and storage nodes.
Controllers and SDN Platforms
Controllers in a software-defined networking (SDN) model centralize network management and enforcement of policies. Administrators define intent and policies through the controller, rather than configuring devices individually. This way, they program the network fabric through APIs or southbound protocols, such as OpenFlow, NETCONF, or gNMI.
Popular platforms include VMware NSX, Cisco ACI, and OpenDaylight, which offer multi-tenancy, automation, service chaining, and dynamic scaling capabilities. SDN improves agility, reduces human error, and integrates with automation pipelines by decoupling the control plane from the data plane.
Monitoring and Telemetry Tools
Visibility is critical for troubleshooting and optimization. Data center networks use telemetry systems that provide real-time streaming data about packet flows, interface statistics, and device health. Tools like sFlow, NetFlow/IPFIX, and ERSPAN capture flow-level insights, while vendors now offer in-band network telemetry (INT) for per-packet tracking.
Centralized monitoring systems use AI/ML to detect anomalies, predict failures, and optimize capacity planning. Effective monitoring reduces mean time to resolution (MTTR) and helps enforce SLAs for latency, jitter, and packet loss.
Artificial intelligence is becoming a more prevalent factor in modern data center networking. To learn more about how to implement AI models in your data center management, refer to our article on AI data center.
Data Center Network Architecture
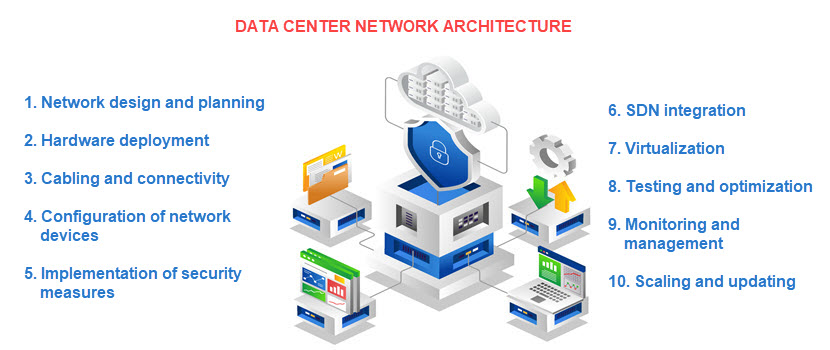
Data center network architecture refers to the structured design that defines how servers, storage, and networking devices are interconnected to deliver fast, reliable, and scalable communication.
Traditional architectures relied on a three-tier hierarchy consisting of core, aggregation, and access layers, which provided clear separation of functions but often introduced latency and oversubscription as workloads scaled and east–west traffic between servers increased with virtualization.
To address the demands of modern applications, most facilities use a leaf–spine architecture, where every leaf switch connects to all spine switches, ensuring predictable latency and uniform bandwidth across the fabric. This design reduces bottlenecks, supports massive east–west traffic, and facilitates scaling by simply adding additional leaf or spine switches.
Beyond the physical topology, modern architecture also incorporates logical overlays and software-defined networking (SDN) to provide flexibility and multi-tenancy. Technologies such as VXLAN with EVPN allow administrators to extend Layer 2 networks across the data center while maintaining isolation between tenants and applications. Network services, such as firewalls, load balancers, and telemetry tools, are often virtualized or integrated directly into the fabric for enhanced efficiency.
Combined with automation and orchestration platforms, these architectures support hybrid and multi-cloud connectivity, enabling enterprises to securely extend workloads beyond the physical data center while maintaining performance and operational consistency.
Visualizing Data Center Networks
At the physical level, data center network visualization highlights the placement of switches, routers, servers, and cabling, helping administrators understand topology, redundancy, and capacity planning. Logical views, on the other hand, illustrate VLANs, VRFs, overlays such as VXLAN, and routing domains, providing insight into how traffic is segmented and flows across the environment.
By mapping both physical and logical aspects, Administrators can quickly identify bottlenecks, underutilized resources, or misconfigurations that might not be obvious from raw configuration files or command outputs.
Modern visualization tools extend beyond static diagrams by integrating real-time telemetry, monitoring, and analytics. Dashboards can display live packet flows, latency, jitter, and bandwidth utilization across various network segments.
Some platforms even use AI-driven analytics to automatically detect anomalies, visualize attack paths, or recommend policy changes. These interactive visualizations facilitate troubleshooting complex environments, validating network designs, and communicating infrastructure layouts to both technical teams and non-technical stakeholders.
Effective visualization not only clarifies how data center networks operate but also validates redundancy strategies to ensure continuous availability even during hardware or link failures. Read more about it in our article on data center redundancy.
Data Center Networking: Best Practices
Strong data center networking practices are essential to ensure performance, reliability, and security at scale.
Here are some essential tasks in data center networking that you should do:
- Implement scalable architecture. Design the network with a leaf–spine or similar scalable topology that provides predictable performance and simplifies expansion.
- Implement redundancy and high availability. Eliminate single points of failure by deploying redundant links, switches, and power sources. Redundancy in both hardware and logical paths guarantees continuous availability during failures or maintenance.
- Segment traffic for security and efficiency. Utilize VLANs, VRFs, and overlays such as VXLAN to isolate workloads, enforce policies, and minimize broadcast domains. Logical segmentation improves security by isolating sensitive applications.
- Leverage automation and orchestration. Automate configuration and lifecycle management using SDN controllers, APIs, or infrastructure-as-code tools. Automation reduces human error, speeds up deployment, and ensures consistent policy enforcement.
- Monitor and analyze network performance. Deploy telemetry, flow analysis, and packet capture tools to gain real-time visibility into network health. Monitoring enables quick detection of anomalies, capacity issues, or security threats.
- Prioritize security. Incorporate firewalls, microsegmentation, and zero-trust principles across your data center. Also, try to enforce security both at the perimeter and within the east–west traffic flows.
- Plan for hybrid and multi-cloud integration. Design connectivity with the flexibility to extend workloads into public or private clouds. Consistent routing, segmentation, and policy management across environments simplifies hybrid deployments.
- Utilize quality of service and traffic prioritization. Classify and prioritize critical traffic, such as storage or latency-sensitive applications, to maintain performance during congestion. QoS ensures fair distribution of resources across workloads.
- Regularly test redundancy. Conduct failure simulations and disaster recovery drills to ensure redundancy mechanisms work as intended. Validation helps confirm that high-availability designs can withstand real-world outages.
These practices enable building a resilient and efficient foundation that sustains performance and reliability.
Data Center Networking Challenges
Data center networking faces unique challenges as organizations demand higher performance, greater scalability, and stronger security to support modern workloads.
Below are some of the most common obstacles that data center operators must address:
- Scalability. As workloads increase and data volumes grow, networks must scale without introducing bottlenecks. Expanding capacity requires careful planning, addressing schemes, and segmentation strategies to avoid performance degradation.
- Latency and performance. Low latency is critical for real-time applications, financial trading, and AI/ML workloads. High east–west traffic within data centers can strain network fabrics, and even minor inefficiencies in routing or buffering can result in latency spikes, jitter, or packet loss that degrades application performance.
- Security threats. With the rise of sophisticated cyber attacks, data centers face constant threats, including DDoS attacks, ransomware, and lateral movement within their network. Protecting workloads requires robust segmentation, encryption, firewalls, and zero trust principles.
- Complexity of management. Modern data centers involve thousands of devices and virtualized elements. Managing configurations, policies, and monitoring across hybrid and multi-cloud environments can quickly become overwhelming without automation and centralized orchestration.
- Cost and resource efficiency. Balancing performance with operational costs remains a persistent challenge. Deploying advanced networking hardware, optical interconnects, and security appliances can be expensive, while inefficient resource usage drives up both capital and operational expenditures.
- Integration with hybrid and multi-cloud environments. Enterprises increasingly rely on hybrid and multi-cloud strategies, which require seamless connectivity between on-premises data centers and external providers. Ensuring consistent performance, security, and policy enforcement across distributed environments is often complex.
- Reliability and redundancy. High availability is essential, but designing redundant systems that can failover without downtime is difficult. Network failures, misconfigurations, or inadequate redundancy planning can result in outages that disrupt critical services.
Addressing these challenges requires a combination of robust architecture, automation, and proactive monitoring.
phoenixNAP's Networking Solutions
phoenixNAP’s networking solutions are designed to address the performance, scalability, and security challenges inherent in modern data center environments. With a global footprint of interconnected facilities, phoenixNAP delivers high-bandwidth, low-latency connectivity that supports demanding workloads, including AI training, real-time applications, and large-scale data analytics.
Our advanced backbone leverages redundant pathways and carrier-neutral interconnects, ensuring that businesses benefit from resilient, always-on connectivity. By combining high-speed switching fabrics with robust peering relationships, phoenixNAP enables seamless east–west and north–south traffic flow, allowing organizations to reduce latency and improve application responsiveness.
Beyond raw performance, phoenixNAP integrates security and flexibility into its networking stack. Built-in DDoS protection, private connectivity options, and dedicated VLANs support the secure segmentation of workloads, ensuring a robust and secure environment. For organizations with more advanced compliance and security needs, phoenixNAP’s Data Security Cloud provides an additional layer of protection.
Gain enterprise-grade security, scalability, and cost efficiency with phoenixNAP’s Data Center as a Service, helping you innovate without the burden of building and maintaining your own facilities.
The Backbone of Digital Infrastructure
Data center networking is the foundation of modern digital services. From the physical fabric of switches, routers, and cabling to the logical overlays, security measures, and automation frameworks, every layer plays a critical role in supporting today’s workloads. By addressing scalability, security, and redundancy, organizations can future-proof their infrastructures, ensuring that their data centers remain secure, efficient, and prepared for growth.