As a non-revenue-generating sector, disaster recovery (DR) is often overlooked in favor of more profit-driven IT initiatives. However, a robust disaster recovery strategy is crucial for ensuring business continuity. DR is a wise investment, paying for itself by preventing potential financial catastrophes.
This article presents key disaster recovery statistics that demonstrate the value of DR initiatives and general readiness for disruptive incidents.
Disaster Recovery Stats
Here are 30 must-know disaster recovery statistics for 2023:
1. Around Half of Companies Have Disaster Recovery Plans
A recent survey found that only 54% of organizations have an established, company-wide disaster recovery plan.
However, 57% of surveyed companies have a second on-prem data center dedicated to disaster recovery.
2. Security Breaches are the Top Cause of Downtime
Around 78% of corporations cite security breaches as the top cause of downtime, according to ITIC's latest Global Server Hardware Security survey.
Additionally, over 80% of respondents see security breaches as the most significant potential threat to the uptime of their on-prem, cloud computing, and network infrastructure.
These figures stand in substantial contrast to ITIC's 2013 survey, where only 22% cited security issues as a top cause of outages.
3. Small Businesses Are the Main Target of Cybercriminals
Small businesses suffer 43% of all data breaches. However, 57% of small business owners believe they are "unlikely" to be a target of a cyber-attack.
4. More Than Half of Small Businesses Close Within Six Months of a Cyber Attack
A recent report from the National Cyber Security Alliance reveals that a staggering 60% of small businesses close within six months of experiencing a cyber-attack.
5. The Majority of Small Businesses Lack Cyber Insurance
Only 9% of small businesses have invested in cyber liability insurance to hedge against cybercrime. Additionally, 83% of small and medium-sized businesses are financially ill-prepared for cyber-attack recovery.
6. Cyber Criminals Exploit Small Businesses as Entry Points
According to a study by the Ponemon Institute, 59% of companies have experienced a data breach attributable to a third-party entity or vendor with whom they shared sensitive info.
Cybercriminals often exploit security flaws in larger companies' external partners, giving them unauthorized access to shared data. This trend underscores the need to exercise vigilance when selecting external partners.
7. Seventy-Three Percent of Organizations Faced a Ransomware Attack in 2022
In a recent study by Barracuda Networks, 73% of organizations reported at least one successful ransomware attack in 2022, with 38% encountering two or more attacks.
The report also reveals that organizations hit with multiple attacks are more inclined to pay the ransom, with 42% of those attacked three times or more electing to meet the criminals' demands. In comparison, only 31% of those hit by a single attack paid the ransom in 2022.
8. Nearly All Ransomware Attacks Try to Infect Backup Systems
Backup servers are generally an adequate safeguard against ransomware attacks. However, 97% of ransomware attacks in 2022 targeted both primary systems and backup repositories.
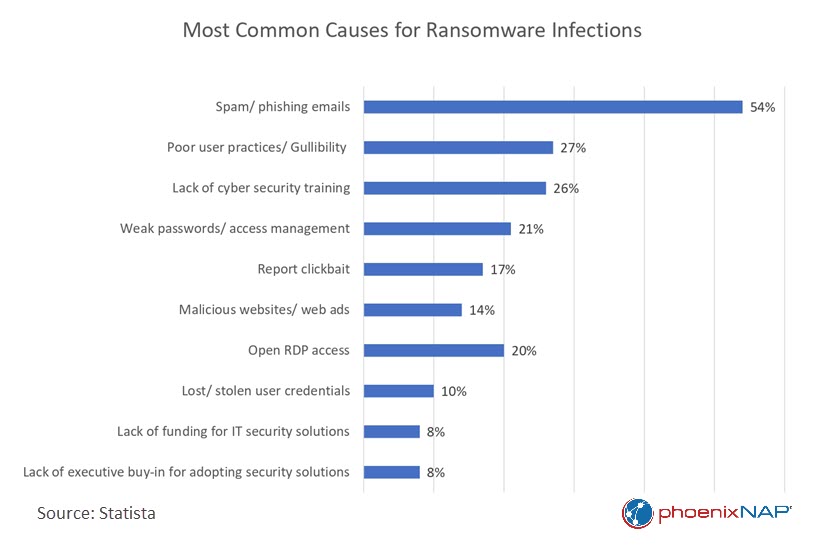
In 2022, approximately 493 million ransomware attacks were reported globally, affecting 71% of all businesses. Read on ransomware statistics to gain insights into the scale, impact, and emerging patterns of these attacks.
9. Businesses Lack Off-Site Backups
Around 42% of medium-sized companies and 30% of large businesses don’t have off-site backups, a UK survey revealed.
Alarmingly, nearly half of the surveyed businesses stored their backups on separate systems within the same office. This localization exposes backups to the same risks and threats that could affect the primary system, making data recovery more problematic.
10. The Majority of Backups Are Incomplete
According to research by Avast, 60% of data backups are incomplete, and backup restores have a 50% failure rate.
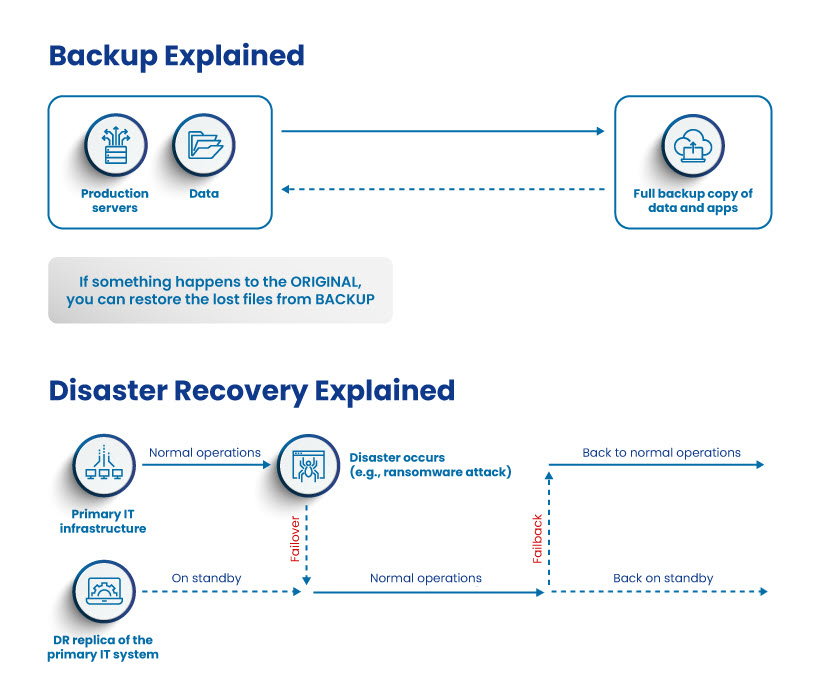
Data backup and disaster recovery are two distinct components of a data protection strategy. Read our backup vs. disaster recovery article to learn more about their differences.
11. Ransomware Causes an Average of 136 Business Hours of Downtime
The most expensive aspect of a ransomware attack is downtime, with recovery expenses typically being ten times the size of the ransom.
After a ransomware attack, the average time-to-recovery was 3.4 weeks, equivalent to making seven round-trip flights from New York to Beijing.
12. Downtime Costs $9,000 Per Minute
Ponemon Institute estimates the average cost of downtime at $9,000 per minute (approx. $500,000 per hour). The average cost of service downtime is so high because it includes not only direct financial losses but also the expenses of lost productivity, missed opportunities, customer dissatisfaction, and long-term reputational damage.
13. More Than Half of Outages Exceed $100,000 in Costs
More than 60% of service outages in 2022 led to at least $100,000 in total losses, a significant increase from 39% in 2019. The Uptime Institute reports that the proportion of outages causing over $1 million in damages rose from 11% to 15% during the same period.
14. Almost All Organizations Have Had an Outage in the Last 3 Years
According to a report by Logic Monitor, 96% of IT organizations worldwide encountered at least one outage between 2019 and 2022.
15. Twenty Percent of Organizations Suffered a Serious Outage in the Last Three Years
A severe outage results in significant financial losses, reputational damage, compliance breaches, or loss of life. According to Uptime's 2022 Data Center Resiliency Survey, one in five organizations reported experiencing a severe outage within the past three years.
16. Frequent Outages Result in Higher Costs
According to Logic Monitor's IT Outage Impact Study, organizations that experience frequent outages incur costs that are 16 times higher compared to companies with fewer instances of downtime.
17. Three Out of Four Organizations Suffer Severe Data Loss
According to a survey by Arcserve, 76% of respondents experienced severe loss of critical data in their organization, with 45% facing permanent data loss.
18. Data Center Hard Drives Have a Life Expectancy of Just Under 3 Years
Data centers face a significant challenge in maintaining the longevity of their hard drives, with the average life expectancy hovering around two years and ten months.
The constant read-write operations, data-intensive processes, and high temperatures put substantial stress on hard drives, impacting their reliability and life span.
19. Cloud Backup Adoption
Around 84% of businesses use cloud backups, with the number increasing to 93% for small and mid-sized businesses. Cloud providers maintain redundant copies of data in multiple data centers, enhancing availability and protection against disasters.
20. Public Cloud's Growing Role
A recent survey by International Data Corporation highlights the growing role of the public cloud in backup and disaster recovery strategies.
Over 88% of respondents see the public cloud as a part of their backup plans, and 91% use it for cloud disaster recovery. Over half of the respondents plan to invest more funds in backup (23%) and disaster recovery (16%) improvements.
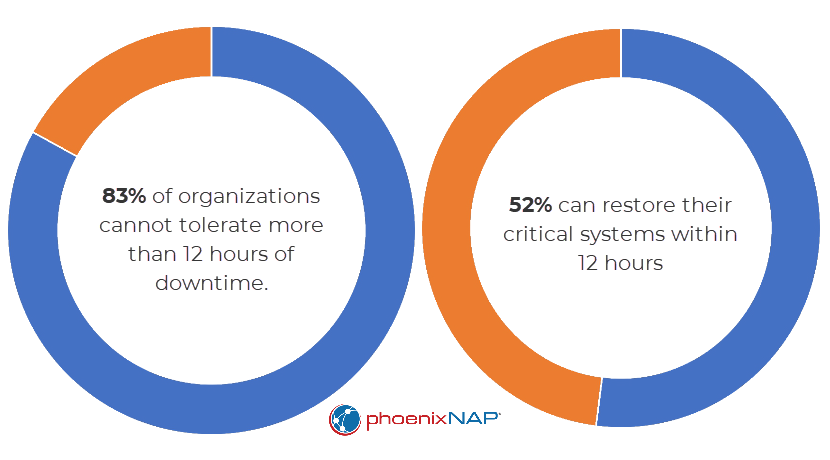
21. Nearly One in Three Businesses Are Unable to Recover Data for a Day or Longer
Almost 83% of organizations can tolerate a maximum of 12 hours of downtime before they experience a negative effect on the business.
However, just 52% are able to restore their critical systems within 12 hours after a severe data loss event, while 29% require a day or more to recover.
22. Data Breach Costs Soar
The latest IBM report reveals an unprecedented surge in the average cost of a data breach, hitting a record high of $4.35 million in 2022. This figure is a 2.6% increase from the previous year and a substantial 12.7% rise from 2020.
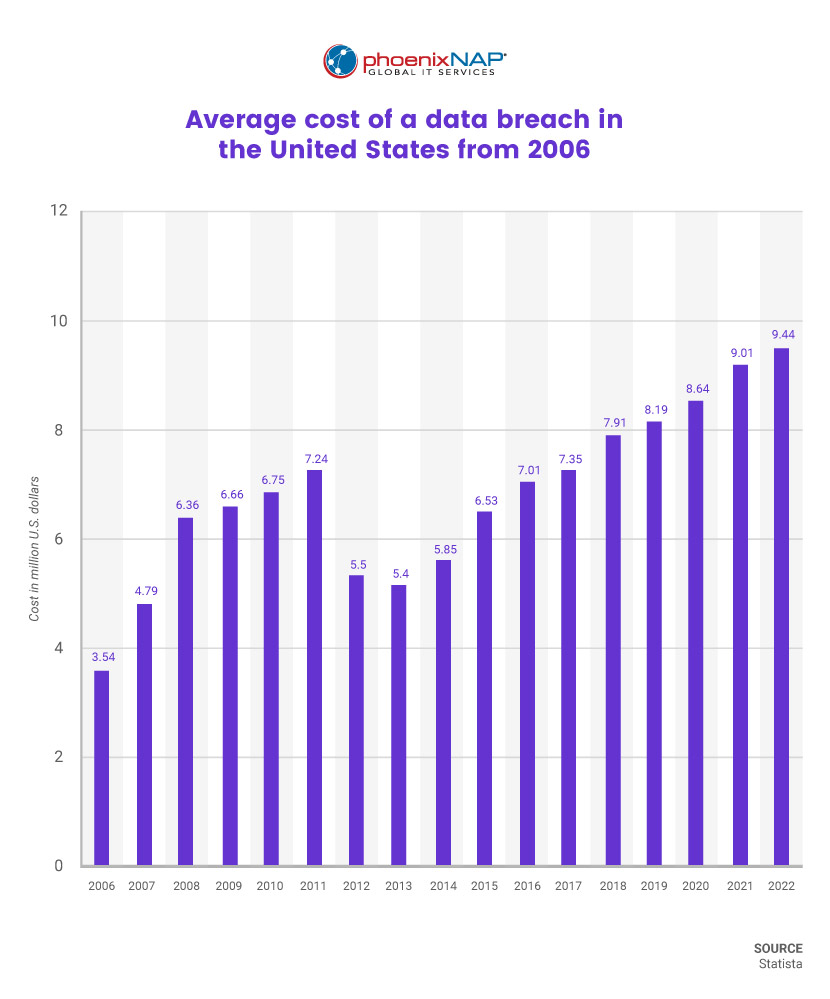
23. US Tops Global Data Breach Costs
The United States continues to lead in data breach costs, with an average of $9.44 million per breach, $5.09 million higher than the global average.
24. Healthcare Sector Bears the Brunt of the Impact
For the twelfth consecutive year, the healthcare sector maintains its position as the industry with the highest average data breach cost ($10.1 million). Healthcare providers saw a 9.4% year-over-year increase in breach costs and a remarkable 42% surge since 2020.
Learn more in-depth about ransomware in healthcare.
25. Over Half of Companies Were Unprepared for the Pandemic
In early 2020, Mercer, a global consultancy firm, conducted a worldwide study to assess companies’ readiness for business continuity during a global pandemic.
Their findings revealed that 51% of businesses lacked any plans or protocols to address a global emergency like COVID-19. Furthermore, 27% of the companies did not have a business continuity plan at the time.
Check out our business continuity vs. disaster recovery article to learn the differences between the two concepts and see how they help organizations stay up and running in times of crisis.
26. Pandemic Leads to Stronger Business Continuity Commitments
According to a survey conducted by Infinite Blue, 81% of respondents reported continuously expanding and enhancing their pandemic plans as previously overlooked dependencies surfaced.
The experiences and insights gained from responding to the pandemic influenced 87% of respondents to "agree" or "strongly agree" that their organizations now hold a more substantial commitment to business continuity planning.
27. Billion-Dollar Climate Disasters
The rising severity of extreme weather events has become a pressing issue for data center operators.
In 2022, the United States faced 18 distinct weather and climate disasters, each causing at least $1 billion in damages. This tally places 2022 in a three-way tie with 2017 and 2011 for the third-highest number of billion-dollar disasters in a single calendar year, trailing behind the 22 events in 2020 and the 20 events in 2021.
28. A Quarter of Businesses Permanently Close After a Disaster
According to a study by the US Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), 25% of businesses do not reopen after a disaster.
29. Global Cybercrime Costs Projected to Skyrocket
Cybersecurity Ventures projects that the global costs of cybercrime will increase by 15% annually over the next five years. By 2025, experts predict that these costs will reach a staggering $10.5 trillion per year, surpassing the $3 trillion recorded in 2015.
This unprecedented growth is the most significant wealth transfer in history and exceeds the yearly damages caused by natural disasters.
30. The Disaster-Recovery-As-A-Service Market Projected to Reach $23 Billion by 2027
Polaris Market Research's new study indicates that the global disaster-recovery-as-a-service (DRaaS) market will grow at a compound annual growth rate of 23.4% and reach $23.3 billion by 2027.
Disaster Recovery Best Practices
The following practices help create a well-rounded DR plan that ensures you deliver services with minimal disruptions during challenging times:
- Use a disaster recovery plan checklist. A checklist ensures consistency and helps cover all critical aspects of DR planning (e.g., risk management, team roles and responsibilities, testing procedures, etc.), leaving no crucial element overlooked.
- Identify your critical IT systems and data. You must know which systems and data are essential for your organization to continue operating. For example, your critical systems might include your email server, website, and CRM system. Your critical data might include customer PII, financial files, and intellectual property.
- Develop a recovery plan for each critical system or data set. Your recovery plan should document the steps you will take to recover each critical system or data set. The plan should also include contact info for key personnel and vendors.
- Test your disaster recovery plan regularly. Surprisingly, only one in four companies regularly tests stheir disaster recovery plan. Testing the plan at least once a year helps ensure that everything is up-to-date and that the team knows how to execute its assignments.
- Have a backup strategy for your critical data. You should store your backup off-site in a secure location. An off-site backup will ensure you can recover data even if the primary data center goes down.
- Use a disaster recovery service provider. A DR service provider helps create and maintain your disaster recovery plan, as well as restore systems and data in the event of a disaster.
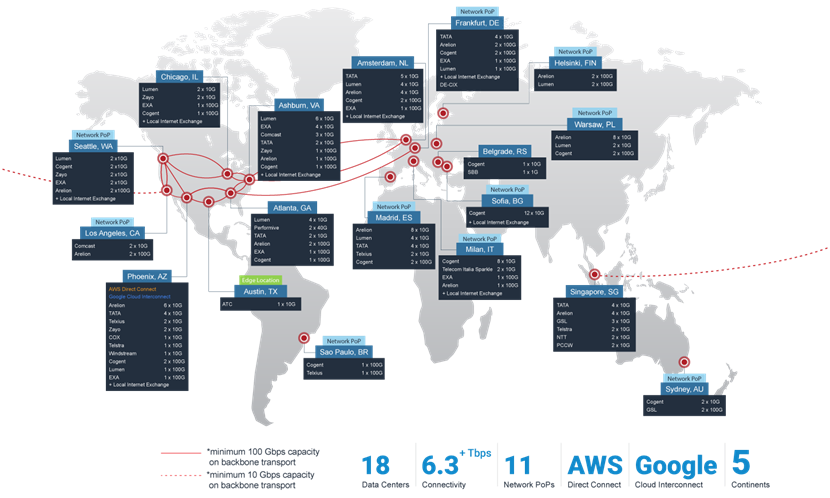
If you prioritize digital resilience, consider our ready-made Disaster-Recovery-as-a-Service solutions. We have a vast network of servers distributed worldwide, spanning North America, South America, Europe, Asia, and Australia. Should a local server failure or disaster occur in one region, our global network servers swiftly restore your services via backups from other locations.
Conclusion
Only 54% of organizations have a company-wide and comprehensive disaster recovery plan. Given the escalating frequency of crippling disruptions, establishing a thorough disaster recovery strategy is a must. Without a DR plan, you are at risk of substantial financial losses in the face of an emergency.
To avoid becoming another cautionary tale of poor planning, implement a robust disaster recovery strategy and significantly improve your odds of successfully navigating through unexpected incidents.